-
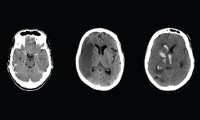
New Blood Test Replaces Costly CT Scan to Detect Head Injury
- Source: News Medical
- 693
- July 27, 2018
-
Blood Test to Suggest Best Possible Treatment for Advanced Prostate Cancer
- Source: ScienceDaily
- 803
- July 26, 2018
-
Curcumin in Turmeric can Treat Glaucoma
- Source: MedicalXpress
- 1,264
- July 26, 2018
-
Invention of Cortisol Detecting Wearable to Measure Stress
- Source: MobiHealthNews
- 680
- July 25, 2018
-
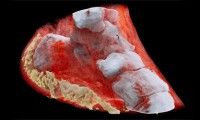
New 3D Color X-Rays to Diagnose Cancer, Heart Disease and More
- Source: Medical Design and Outsourcing
- 1,216
- July 20, 2018
-
Hackers Breach LabCorp Network, Patient Records at Risk
- Source: HealthcareIT News
- 848
- July 20, 2018
-
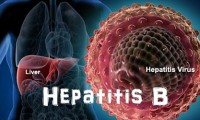
TREAT-B – Blood Test to Detect Hepatitis B Well in Advance
- Source: MedIndia
- 404
- July 18, 2018
-
Recent Developments in HBV Diagnosis & Treatment
- Source: News Medical
- 678
- July 9, 2018
-
Novel Blood Test to Determine Right Time for Drug Administration
- Source: The Verge
- 697
- July 6, 2018
-
Zika Virus Detection Using Smartphone Based NBC Detection Tool
- Source: The Verge
- 1,551
- July 6, 2018
your submission has already been received.
OK
Subscribe
Please enter a valid Email address!
Submit
The most relevant industry news & insight will be sent to you every two weeks.