-
Ipsen joins the ADC club with deal worth up to $900m
- Source: drugdu
- 153
- April 4, 2024
-
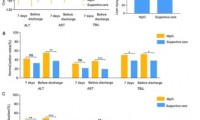
Latest Research Results of Magnesium Isoglycyrrhizinate GM-DILI-002 Announced
- Source: drugdu
- 202
- April 4, 2024
-
Gilead, Xilio Therapeutics Ink Exclusive Licensing Agreement to Develop Early Phase Tumor-Activated IL-12
- Source: drugdu
- 96
- April 3, 2024
-
IASO Bio Announces NMPA’s IND Approval for Equecabtagene Autoleucel in Second- and Third-Line Treatment of Multiple Myeloma
- Source: drugdu
- 89
- April 3, 2024
-
Hengrui’s Clinical Application for New Drug Indicated for Psoriasis Approved
- Source: drugdu
- 92
- April 2, 2024
-
Altamira Therapeutics partners with Univercells Group on nanoparticle-delivered mRNA vaccines
- Source: drugdu
- 79
- April 2, 2024
-
Strand Therapeutics develops new class of mRNA molecules for cancer
- Source: drugdu
- 82
- April 1, 2024
-
Blood Analysis Predicts Sepsis and Organ Failure in Children
- Source: drugdu
- 96
- March 29, 2024
-
Testing Method Could Help More Patients Receive Right Cancer Treatment
- Source: drugdu
- 93
- March 26, 2024
your submission has already been received.
OK
Subscribe
Please enter a valid Email address!
Submit
The most relevant industry news & insight will be sent to you every two weeks.