Latest Research Results of Magnesium Isoglycyrrhizinate GM-DILI-002 Announced
April 4, 2024
Source: drugdu
 913
913
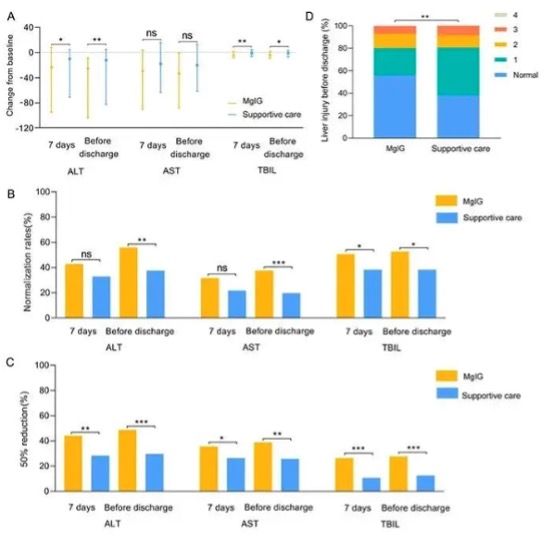
Recently, the 33rd Annual Meeting of the Asia-Pacific Association for the Study of the Liver (APASL 2024) presented a study (GM-DILI-002) analyzing the efficacy of Chiatai Tianqing magnesium isoglycyrrhizinate (MgIG) in the treatment of liver injury associated with a novel antitumor drug based on real-world data from China, and the results of the study (No. 100906 and No. 100910) fill the evidence-based Gap.
This real-world, non-interventional, multi-center, retrospective study was conducted in three main settings. The study was based on an e-diagnostic system that screened and analyzed data from a population of 1,710 patients who met international liver biochemical criteria related to DILI (drug-induced liver injury) during treatment with novel antineoplastic agents.
In recent years, the emergence of new antitumor drugs, such as molecular targeting and immune checkpoint inhibitors, has led to a continuous improvement in the survival of tumor patients, but at the same time the problem of drug-related adverse reactions, especially drug-related liver injury, has gradually come to the fore. Currently, there is a lack of international consensus protocols other than GC or discontinuation of antitumor drugs for patients who develop targeted and immunotherapy-related liver injury.
In the actual treatment process, GC often appears to be restricted due to the existence of patient comorbidities, and its adverse effects can also put antitumor therapy into a dilemma.The chemical structure of MgIG is similar to glucocorticoids, and the results of this study showed that there was no significant difference in the effect of GC compared with MgIG alone, while MgIG combined with GC had a better effect than that of GC combined with SC, with a more rapid and greater decrease in liver function indexes. MgIG combined with GC had a better effect than GC combined with SC, and liver function indexes decreased faster and more rapidly. Meanwhile, MgIG has anti-inflammatory effect, which can stabilize hepatocytes, and the overall recovery of liver will be better.
The results of this study confirm that MgIG fills the gap of evidence in the treatment of liver injury associated with novel antitumor drugs in the clinic, and its efficacy is comparable to that of GC when used alone, and it benefits more when combined with hormone therapy. In the future, further prospective, RCT studies will be conducted to confirm the preliminary conclusions obtained so far, to provide clinicians with better evidence to guide the choice of DILI drug therapy in clinical practice, and ultimately to enable patients to achieve a better survival and help reduce the burden of tumor disease in China.
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzA5NDE4ODc2MA==&mid=2650365988&idx=1&sn=5e4ebe11b660aa151be448661884823a&chksm=885fa593bf282c85cea957446b0e8b82cfe39cd692dc0b754cb38f9329a43fa1f7bce7e4c136&mpshare=1&scene=1&srcid=0403Y6MgyuJkZQwMKodMiSXN&sharer_shareinfo=43941bce77e13104f15899c0ec0a833d&sharer_shareinfo_first=43941bce77e13104f15899c0ec0a833d#rd
Read more on
- Gusekirumab Injection Accepted by CDE, Multiple Pipelines Advancing Simultaneously March 4, 2026
- Yifan Pharmaceutical’s teriparatide injection has been accepted by the CDE (Center for Drug Evaluation), adding a new domestic player to the osteoporosis treatment field March 4, 2026
- //news.yaozh.com/archive/47318.html PD-1 sales surge March 4, 2026
- A major breakthrough! Roche’s oral BTK inhibitor achieves its third Phase III clinical trial victory, a game-changer in the multi-billion dollar MS (manufactured pharmaceuticals) market. March 4, 2026
- GB19 Injection Approved for Clinical Trials of Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus March 4, 2026
your submission has already been received.
OK
Subscribe
Please enter a valid Email address!
Submit
The most relevant industry news & insight will be sent to you every two weeks.



