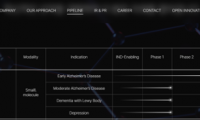
-
$1.4 billion deal highlights the future of Alzheimer’s disease therapy
- Source: drugdu
- 57
- November 5, 2024
-
Just now! The first Chinese generic version of the “blockbuster Alzheimer’s drug” was released
- Source: drugdu
- 68
- September 28, 2024
-
Blood Test Predicts Alzheimer’s Disease with Over 90% Accuracy
- Source: drugdu
- 121
- August 1, 2024
-
Advanced Blood Test to Spot Alzheimer’s Before Progression to Dementia
- Source: drugdu
- 116
- May 10, 2024
-
$770 Million! AriBio authorizes Marketing Rights for a Drug to Treat Alzheimer’s Disease in China
- Source: drugdu
- 143
- March 28, 2024
-
Groundbreaking pTau217 Blood Test as Accurate as Brain Imaging or CSF Testing in Diagnosing Alzheimer’s
- Source: drugdu
- 152
- March 23, 2024
-
Cerebrospinal Fluid Testing of Alzheimer’s Patients to Help Identify Disease Molecular Subtype
- Source: drugdu
- 169
- January 17, 2024
-
Stem-cell-derived brain cells hold promise for Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s research
- Source: drugdu
- 113
- November 21, 2023
-
Photobiomodulation in sleep has more therapeutic effects for Alzheimer’s disease than in wakefulness
- Source: drugdu
- 213
- September 25, 2023
-
Muscle-Building Supplement May Help Protect Memory and Prevent Alzheimer’s Disease
- Source: drugdu
- 204
- July 24, 2023
your submission has already been received.
OK
Subscribe
Please enter a valid Email address!
Submit
The most relevant industry news & insight will be sent to you every two weeks.