-
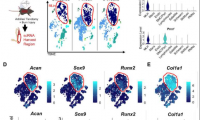
Researchers discover critical protein for common bone growth disorder
- Source: drugdu
- 140
- April 19, 2023
-
Discovery suggests a new way to treat spinal muscular atrophy
- Source: drugdu
- 129
- April 19, 2023
-
Study reveals the risk factors associated with developing long Covid
- Source: drugdu
- 121
- April 19, 2023
-
FDA gives approval to cell therapy Omisirge for blood cancer patients
- Source: drugdu
- 105
- April 19, 2023
-
EPA proposes new ethylene oxide rules for medical device sterilization
- Source: drugdu
- 231
- April 19, 2023
-
Odds of Heart Attack Six Times Higher With Flu Diagnosis
- Source: drugdu
- 116
- April 19, 2023
-
Higher intake of flavonols linked to lower risk of frailty onset in adults
- Source: drugdu
- 106
- April 19, 2023
-
Binocular visual stimulation followed by sleep helps treat common vision problem in children
- Source: drugdu
- 120
- April 19, 2023
-
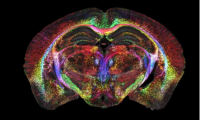
Brain images just got 64 million times sharper
- Source: drugdu
- 121
- April 18, 2023
-
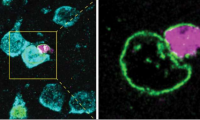
Researchers discover how some brain cells transfer material to neurons in mice
- Source: drugdu
- 144
- April 18, 2023
your submission has already been received.
OK
Subscribe
Please enter a valid Email address!
Submit
The most relevant industry news & insight will be sent to you every two weeks.