-
Innovative C. Difficile Diagnostic Test Provides Both GDH and Toxin Results within 30 Minutes
- Source: drugdu
- 70
- July 18, 2024
-
Diagnostic Test Could Detect Elusive Neuro Disorder Using Tiny Drop of Spinal Fluid
- Source: drugdu
- 103
- July 10, 2024
-
Groundbreaking Molecular Diagnostic Kit to Provide Lyme Disease Detection in Minutes
- Source: drugdu
- 92
- June 4, 2024
-
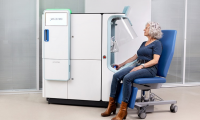
Robotic Blood Drawing Device to Revolutionize Sample Collection for Diagnostic Testing
- Source: https://www.labmedica.com/pathology/articles/294801059/robotic-blood-drawing-device-to-revolutionize-sample-collection-for-diagnostic-testing.html
- 151
- May 4, 2024
-
Enhanced Rapid Syndromic Molecular Diagnostic Solution Detects Broad Range of Infectious Diseases
- Source: https://www.labmedica.com/microbiology/articles/294801045/enhanced-rapid-syndromic-molecular-diagnostic-solution-detects-broad-range-of-infectious-diseases.html
- 95
- May 4, 2024
-
First of Its Kind Universal Tool to Revolutionize Sample Collection for Diagnostic Tests
- Source: drugdu
- 80
- May 1, 2024
-
Low-Cost Point-Of-Care Diagnostic to Expand Access to STI Testing
- Source: drugdu
- 85
- April 23, 2024
-
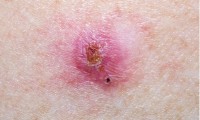
Deep Learning Powered AI Algorithms Improve Skin Cancer Diagnostic Accuracy
- Source: drugdu
- 113
- April 18, 2024
-
New Diagnostic System Achieves PCR Testing Accuracy
- Source: drugdu
- 120
- April 11, 2024
-
Automated Multiplexing Molecular Diagnostic Platform Revolutionizes Infectious Disease Diagnostics
- Source: drugdu
- 142
- March 8, 2024
your submission has already been received.
OK
Subscribe
Please enter a valid Email address!
Submit
The most relevant industry news & insight will be sent to you every two weeks.