Latest Developments in New Drugs for Kidney Disease
November 25, 2025
Source: drugdu
 151
151
In the vast and complex field of chronic kidney disease, IgA nephropathy (IgAN) has long been considered a "silent corner." However, with a deeper understanding of its pathogenesis and breakthroughs in treatment, this once-neglected disease area is now showing renewed vitality.
01 Changes in the Times
The unique aspect of IgA nephropathy lies in its complex pathogenesis. Traditionally, it was considered an autoimmune disease, but recent studies have found that its pathogenesis involves multiple steps, including mucosal immune abnormalities, the production of galactose-deficient IgA1, the formation of autoantibodies, and the deposition of immune complexes, ultimately leading to kidney tissue damage through complement activation.
The elucidation of this mechanism provides a clear direction for the development of targeted drugs. Current treatment strategies mainly focus on four pathways: (1) Mucosal immune regulation: targeting the initial stage of the pathogen immune response; (2) Inhibition of the endothelin-1 (ET-1) pathway: improving glomerular hemodynamics and fibrosis; (3) Complement system blockade: inhibiting the terminal damage pathway; (4) B cell targeted therapy: reducing the production of abnormal antibodies from the source.
Targeted drugs developed based on these mechanisms are fundamentally changing the treatment paradigm for IgA nephropathy.
02 A Hundred Billion Yuan Blue Ocean Awaits Exploration
The patient population is large and the diagnosis rate is improving: There are approximately 10 million IgA nephropathy patients worldwide, with about 5 million in my country, and more than 100,000 new cases diagnosed each year. With the widespread adoption of kidney biopsy technology and increased awareness among physicians, this large patient base provides a solid foundation for the innovative drug market.
Treatment needs are far from being met: Despite the large number of patients, traditional treatments are limited to RAS inhibitors and immunosuppressants, with limited efficacy and significant side effects. 20%–40% of patients may gradually progress to end-stage renal disease within 10–20 years, urgently requiring more effective and specific treatments.
The market growth prospects are clear: According to PharmNet Consulting, the global market size for targeted drugs for IgA nephropathy is currently about US$1.2 billion, and is expected to grow to US$1.6 billion by 2026. By 2030, the global market size is expected to exceed US$10 billion, with the Chinese market expected to reach RMB15-20 billion.
03 The Four Heavenly Kings each display their unique abilities
Currently, four targeted therapies have been approved globally (most initially through conditional/accelerated approval) for IgA nephropathy, and three have been approved in China (only sparsentan is not yet approved domestically). Budesonide enteric-coated capsules are the world's first and currently only targeted therapy specifically addressing the root cause of IgA nephropathy (mucosal immunity). Ipcomycin hydrochloride capsules are the world's first approved oral complement factor B inhibitor for the treatment of IgA nephropathy. Initially approved in the US for paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH), IgA nephropathy was subsequently expanded to include this indication.
04 The "Three Musketeers of Domestic Products" Lead a New Wave
Currently, there are more than 70 IgA nephropathy drugs in clinical trials worldwide (about 40 of which are in China).
Chinese innovative pharmaceutical companies are rapidly expanding their presence in the field of IgA nephropathy, and three internationally competitive products deserve close attention:
(1) HRS-5965: HRS-5965 is a complement factor B inhibitor from Hengrui Medicine, which can reduce proteinuria and delay the progression of kidney disease. Currently, Phase III clinical trials (for IgA nephropathy) are underway globally and in China. In 2025, this drug will be included in the list of proposed breakthrough treatment products. The results of the Phase II clinical trial of HRS-5965 showed that at week 12, the changes in 24-UPCR (g/g) from baseline in the HRS-5965 25, 50 and 75 mg groups were -27.9%, -30.7% and -39.5%, respectively, while the placebo group was -2.9% (P=0.0501, 0.0056 and 0.0002, respectively); the changes in eGFR from baseline in the HRS-5965 25, 50 and 75 mg groups and the placebo group were -0.84, 2.74, 4.26 and 1.41 ml/(min·1.73m2), respectively.
(2) Telitacicept: Telitacicept is the world's first and first-in-class injectable recombinant B lymphocyte stimulating factor (BLyS)/proliferation inducing ligand (APRIL) dual-target novel fusion protein product independently developed by Rongchang Biotechnology. It has been approved for indications such as systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. In the field of IgA nephropathy, it is currently applying for marketing approval. The latest clinical research results show that after 39 weeks of treatment, compared with the placebo group, the 24-hour UPCR of patients in the Telitacicept group was significantly reduced by 55% (P<0.0001), while showing good safety and tolerability.
(3) SC0062: SC0062 is a highly selective ETA receptor antagonist developed by Wuxi Zhikang Hongyi. It is currently in Phase III clinical trials globally and in China. The latest clinical study results show that, compared with the placebo group, all SC0062 dose groups reduced UPCR throughout the treatment process. At week 12, the placebo-corrected geometric mean change (95% confidence interval) of UPCR in the SC0062 5, 10 and 20 mg groups were -27.6% (-43.0 to -8.2), -20.5% (-37.4 to 1.0) and -38.1% (-51.4 to -21.0), respectively; at week 24, they were -22.4% (-42.2 to 4.3), -30.9% (-48.6 to -7.0) and -51.6% (-64.2 to -34.6), respectively.
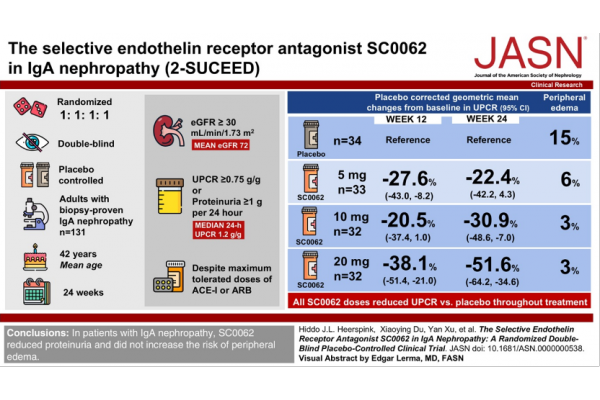 Figure 2. Clinical study methods and results of SC0062
Figure 2. Clinical study methods and results of SC0062
Image source: References
05 Conclusion
The booming market for IgA nephropathy is no accident, but rather a natural manifestation of the precision medicine approach in the field of kidney disease. With a deeper understanding of the disease mechanisms and the continuous emergence of targeted drugs, IgA nephropathy treatment is entering its golden age. Future competition will no longer be limited to a single efficacy indicator, but will be a comprehensive contest of efficacy, safety, convenience, and pharmacoeconomics. Products that achieve the best balance across these four dimensions will stand out in this multi-billion dollar market and become true blockbuster drugs.
For pharmaceutical professionals, IgA nephropathy, a niche and promising field, presents a rare window of opportunity. With advancements in diagnostic technology and evolving treatment philosophies, this once-overlooked area is becoming a hotbed for innovative drug development, and its trajectory may offer valuable insights for other rare and specialized disease areas.
https://news.yaozh.com/archive/46345.html
By editorRead more on
- a full look at 15 blockbuster drugs. February 28, 2026
- EMA CHMP Recommends EU Approval of Henlius’ Pertuzumab Biosimilar HLX11 February 28, 2026
- Akeso Biopharma’s autoimmune pipeline reaches another milestone! Mandocizumab submits application for market approval, targeting a market worth tens of billions. February 28, 2026
- $2.1 billion! Novo Nordisk reaches new cooperation agreement February 28, 2026
- After Eli Lilly and Novo Nordisk, who most resembles the “Third Brother of Weight Loss”? February 28, 2026
your submission has already been received.
OK
Subscribe
Please enter a valid Email address!
Submit
The most relevant industry news & insight will be sent to you every two weeks.



