-
NIH grants support Kessler Foundation scientists to advance research on neglect dyslexia and autism
- Source: drugdu
- 114
- September 13, 2023
-
EAE Hub Model Reduces Barriers to Early Autism Diagnosis
- Source: drugdu
- 133
- July 20, 2023
-
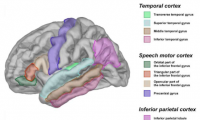
Language impairment in autism associated with gray matter volume
- Source: drugdu
- 136
- April 27, 2023
-
Common ear, nose, and throat issues in preschoolers may be linked to later autism risk
- Source: drugdu
- 119
- April 26, 2023
-
Debunking Myths about Vaccines and Autism
- Source: Ddu
- 914
- August 28, 2018
-
Google Glass Eye-Wearable to Enhance Social Skills among Autism Kids
- Source: MedPageToday
- 1,091
- August 6, 2018
-
Blood Test to Detect Autism
- Source: HealthLine
- 766
- July 3, 2018
-
Autism Spectrum Disorder Prediction Via Baby Teeth
- Source: Ddu
- 577
- June 11, 2018
-
Autism Screening App on iOS by Duke University
- Source: Ddu
- 564
- June 7, 2018
your submission has already been received.
OK
Subscribe
Please enter a valid Email address!
Submit
The most relevant industry news & insight will be sent to you every two weeks.