structural mechanisms, clinical advantages, opportunities and challenges
March 6, 2025
Source: drugdu
 566
566
 Small molecule drug conjugates (SMDCs) are a new type of targeted therapy drug that originated from the optimization exploration of traditional chemotherapy and antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). They aim to improve efficacy and reduce systemic toxicity through precise delivery, and have advantages in targeting, safety, and cost.
Small molecule drug conjugates (SMDCs) are a new type of targeted therapy drug that originated from the optimization exploration of traditional chemotherapy and antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). They aim to improve efficacy and reduce systemic toxicity through precise delivery, and have advantages in targeting, safety, and cost.
Currently, no SMDC has been approved for marketing in the world. About 10 candidate drugs are in the clinical stage. Their indications are mainly solid tumors. They provide new strategies for drug-resistant tumors and are expected to expand to other disease areas.
SMDC combines the flexibility of small molecule drugs with the synergistic potential of conjugation technology, promoting the evolution of tumor treatment towards high efficiency and low toxicity, and becoming a potential branch in the conjugated drug track.
Mechanism of action of SMDC
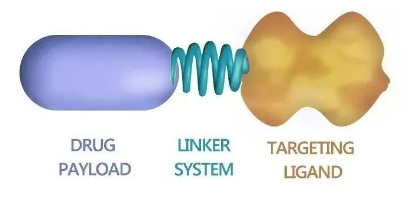
Small molecule drug conjugates (SMDCs) consist of three parts: small molecule targeting ligands, linkers, and payload drugs.
Its mechanism of action is basically the same as that of ADC drugs. It uses small molecule ligands to specifically recognize receptors or transporters overexpressed on the surface of tumor cells, and delivers cytotoxic drugs into target cells through endocytosis, thereby achieving precise killing .
Small molecule targeting ligands
The targeting ligand of SMDC is a small molecule compound, which plays a role in SMDC similar to that of ADC antibodies. The selection of SMDC ligands needs to take into account issues such as binding affinity, selectivity and compound size. Therefore, they are mainly derived from derivatives of natural ligands, such as folic acid, prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) inhibitors or integrin antagonists. Compared with ADC ligands, the selection range is relatively small, which is the main limitation of the current development of SMDC.
Currently, SMDC drugs targeting folate receptors are the most studied. Folate receptors are highly expressed in many solid tumors (such as ovarian cancer and lung cancer). SMDC with folate as a ligand can be efficiently enriched in tumor tissues through receptor-mediated endocytosis.
Linker
The linker of SMDC is similar to ADC, which is the link between small molecule targeting ligand and loaded drug. Its design determines the stability and drug release efficiency of SMDC. Currently, the SMDC drugs under development mainly use two technical routes: enzyme-sensitive linkers and disulfide-bond-based linkers.
Drug Loading
The payload drugs of SMDC currently under development are mainly cytotoxic chemotherapy drugs, such as camptothecin derivatives (SN-38), microtubule inhibitors (MMAE) and topoisomerase inhibitors, etc. In addition, some studies have tried to use radionuclides (such as actinium-225) or immunomodulators as payloads to expand its therapeutic range.
Clinical advantages of SMDC
First, the clinical advantages of SMDC are mainly based on its small molecule characteristics.
Small molecule targeting ligands enable SMDC to easily penetrate and diffuse more evenly into tumor tissue, giving it higher tumor penetration. Small molecules will not accumulate in tumors and other normal cells, and a small number of off-target drugs will be quickly excreted from the body, thereby reducing toxicity to normal cells. At the same time, SMDC theoretically will not be immunogenic, and safety control is easier to achieve.
In addition, compared with antibody drugs, SMDC is easy to control the synthesis process and cost, and its industrial operation is simple.
Higher tumor penetration
Compared with ADC (molecular weight of approximately 150kDa) and PDC (molecular weight of approximately 5-10kDa), the molecular weight of SMDC is usually less than 1kDa. It can quickly penetrate solid tumor tissues through passive diffusion, overcome the delivery bottleneck of traditional macromolecular drugs, and have better cell permeability in solid tumors.
Renal metabolism and low immunogenicity
SMDC is mainly metabolized through the kidneys and has a short half-life, which reduces the accumulation of drugs in the liver and bone marrow. A small number of off-target drugs will also be quickly excreted from the body, reducing toxicity to normal cells and having better in vitro and in vivo stability.
For example, the folate receptor SMDC Vintafolide showed low hepatotoxicity in clinical trials [2]. At the same time, SMDC is theoretically not immunogenic, making its safety control easier to achieve.
Lower production costs
The chemical synthesis process of small molecules is mature, and the production cost is significantly lower than that of antibodies or peptides. It is easier to scale up production and control costs.
Precise payload
The ratio of the payload to the antibody in ADC drug molecules is usually uncertain, so the intracellular payload may fluctuate; the small molecule targeting ligand and payload of SMDC usually have an accurate ratio.
Analysis of SMDC's global and Chinese pipelines
Compared with the hot ADC track and the breakthroughs made by PDC and RDC in technology and market, SMDC's research and development has not yet achieved impressive results.
At present, no SMDC has been approved for marketing at home or abroad, but about a dozen drugs have entered the clinical research stage, of which about 7 have entered the clinical phase II research, and the overall situation is in the early stage of clinical research and development. Compared with other new conjugate drugs, RDC has 11 drugs approved for marketing, of which Lutathera's sales in 2023 will reach US$605 million, and more than 270 RDC new drugs are in clinical trials and application for marketing; PDC has two drugs approved, and there are about 20 pipelines entering the clinical trial stage worldwide, and many pipelines have entered the late clinical stage.
Currently, the target diversity in SMDC's pipeline is also relatively low, mainly concentrated in several targets such as AKR1C3, KRAS G12D, and Tubulin.
Although there are relatively few companies with overseas layout, several representative products in the field are also worth mentioning:
Vintafolide (Endocyte): As the most advanced product in the global clinical stage, it entered the registration application stage as early as 2014 and received conditional approval from the European Medicines Agency in 2014. However, it was ultimately declared a failure due to failure to reach the primary endpoint of progression-free survival. Endocyte then completely abandoned the SMDC field and turned to research on other types of conjugated drugs. The famous Lutathera is the result of this switch, with global sales reaching US$724 million in 2024.
In terms of domestic companies, there are relatively more companies investing in the SMDC field compared to overseas companies, and the competition is also greater. The more representative ones include Aixindawei, Tongyi Pharmaceutical, etc.
Aixindawei focuses on the research and development of innovative SMDC drugs. Currently, two SMDC drug pipelines have entered Phase II clinical research, of which AST-001 is its key pipeline. In a Phase I clinical study of solid tumors, more than 10 types of advanced solid tumor patients with different tumor types were widely enrolled. Among the patients who met the target requirements, the disease control rate reached 66.7%, and the ORR was 33.3%. It fully demonstrated the broad-spectrum anti-tumor characteristics of AST-001. In terms of safety, most treatment-related adverse events (TRAEs) were grade 1-2, which were controllable and manageable. AST-3424 is the world's first SMDC that relies on AKR1C3 enzyme activation. The results of its Phase II clinical trial showed that as a late-line drug, AST-3424 has good effectiveness in the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma, especially for HCC subjects who have progressed after immunotherapy, and can still prolong their survival.
Tongyi Pharmaceutical also has several SMDC drugs under development, among which CBP-1008 and CBP-1019 are the most promising. In a global multicenter, open-label Phase I/II clinical trial, CBP-1019 enrolled 10 patients with advanced/metastatic EC. The results showed that at a dose level of 3.0 mg/kg, 7 out of 9 patients with advanced/metastatic EC had at least one tumor assessment after dosing, with an objective response rate (ORR) of 42.9% and a disease control rate (DCR) of 100%.
CBP-1008 is a global dual-ligand SMDC targeting folate receptor α (FRα)/transient receptor potential cation channel 6 protein (TRPV6). Its Phase I trial in patients with advanced solid tumors includes platinum-resistant high-grade serous ovarian cancer (HGSOC), clear cell ovarian cancer (OCCC), metastatic triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) and other solid tumors. It was granted Fast Track status by the FDA in October 2024.
As for the clinical effectiveness data of the above-mentioned SMDC series pipeline, in addition to data observations within the SMDC field, the comparison between SMDC and other technical fields such as chemotherapy, small molecule targeted inhibitors and ADC is actually more important.
At present, since SMDC is still in the early clinical stage, many data are not statistically significant. But on the whole, the ORR and DCR data currently displayed by some products are not inferior to ADC or the new generation of PARP inhibitors. In fact, due to its production cost, tumor penetration and other characteristics, there is more room for imagination.
SMDC's development prospects
The research and development of SMDC drugs is currently in the early exploratory stage, and the selection of small molecule ligands is the main difficulty in the current SMDC development.
SMDC ligands are mainly derivatives of naturally derived ligands. Compared with ADC ligands, the selection range is smaller, suitable receptors and ligands are difficult to obtain, and the targets and indications are relatively narrow. Therefore, optimizing existing designs, expanding the selection range of small molecule ligands, and expanding the coverage of targets and indications are key strategies for SMDC to break through development bottlenecks.
summary
With its small molecule characteristics, SMDC has shown significant advantages in tumor penetration, production cost and safety, and has become an important branch in the field of conjugated drugs.
Currently, SMDC clinical research and development is limited by the narrow selection of small molecule targeted ligands, and drug research and development as a whole is still in the early exploration stage, lagging behind the development process of other types of conjugated drugs. Domestic companies already have several SMDC pipelines entering Phase II clinical research and have the potential to become FICs in the SMDC field.
In the future, more companies may participate in the research and development of SMDC, continuously improving the technical bottlenecks of existing products, so that SMDC is expected to provide more precise treatment solutions for solid tumors and refractory cancers.
https://news.yaozh.com/archive/45086.html
By editorRead more on
- Phase III clinical trial of vetcotozumab completes patient enrollment February 9, 2026
- The first long-acting coagulation factor VIII, has officially entered the Chinese mainland market. February 9, 2026
- 17.9 billion yuan! A top-selling topical medication emerges. February 9, 2026
- Turnaround! Generic drug giant successfully “revived” February 9, 2026
- Novartis’s first-ever autoimmune drug has been submitted for marketing approval in China. February 9, 2026
your submission has already been received.
OK
Subscribe
Please enter a valid Email address!
Submit
The most relevant industry news & insight will be sent to you every two weeks.



