-
Type 2 diabetes patients who were physically active in the afternoon have greater reductions in blood sugar
- Source: drugdu
- 124
- May 30, 2023
-
Centre for Genomic Regulation and Almirall join forces on skin cancer treatments
- Source: drugdu
- 124
- May 29, 2023
-
A new antibiotic, discovered with artificial intelligence, may defeat a dangerous superbug
- Source: CNN
- 136
- May 28, 2023
-
Sudden infant death syndrome may have biologic cause
- Source: drugdu
- 110
- May 26, 2023
-
Neuralink competitor Paradromics gets one step closer to FDA approval for its brain implant
- Source: drugdu
- 123
- May 21, 2023
-
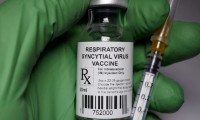
FDA advisors recommend Pfizer’s RSV vaccine for infants but raise safety concerns
- Source: drugdu
- 115
- May 20, 2023
-
Is Parkinson’s a Military Base’s Toxic Legacy?
- Source: drugdu
- 122
- May 19, 2023
-
Occasional cannabis use during pregnancy may be enough to impact fetal growth significantly
- Source: drugdu
- 109
- May 17, 2023
-
NHS misses targets in England to tackle care backlogs
- Source: drugdu
- 115
- May 15, 2023
-
A machine-learning approach for the early diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease
- Source: https://www.news-medical.net/news/20230511/A-machine-learning-approach-for-the-early-diagnosis-of-Parkinsons-disease.aspx
- 109
- May 14, 2023
your submission has already been received.
OK
Subscribe
Please enter a valid Email address!
Submit
The most relevant industry news & insight will be sent to you every two weeks.