-
Amid high demand, Novo Nordisk temporarily throttles US supply of low-dose Wegovy
- Source: drugdu
- 131
- May 9, 2023
-
Acelyrin follows Kenvue with largest IPO for a biotech startup since 2021
- Source: drugdu
- 119
- May 6, 2023
-
New study reveals the best diets for a healthy heart
- Source: drugdu
- 138
- May 5, 2023
-
Long siesta-takers have higher BMIs and more likely to have metabolic syndrome
- Source: drugdu
- 139
- May 1, 2023
-
Do ketogenic diets elevate low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels?
- Source: drugdu
- 197
- April 29, 2023
-
Eli Lilly to sell low blood sugar drug Baqsimi to Amphastar in deal worth over $1bn
- Source: drugdu
- 168
- April 28, 2023
-
New research suggests that french fries may be linked to depression
- Source: drugdu
- 130
- April 28, 2023
-
High-protein diet counters adaptive thermogenesis in prediabetic individuals
- Source: drugdu
- 141
- April 27, 2023
-
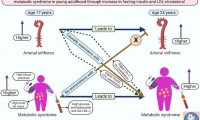
Arterial stiffness may be a novel risk factor for childhood and adolescent metabolic disease
- Source: drugdu
- 108
- April 27, 2023
-
Study shows no significant cognitive benefit of adhering to Mediterranean diets regardless of calorie intake
- Source: drugdu
- 132
- April 27, 2023
your submission has already been received.
OK
Subscribe
Please enter a valid Email address!
Submit
The most relevant industry news & insight will be sent to you every two weeks.