-
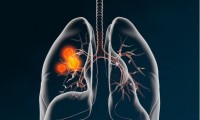
Merck and Moderna to Launch Trial of mRNA-4157 Plus Keytruda in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Source: drugdu
- 98
- December 13, 2023
-
AstraZeneca Cancer Drug Is First in Class, But FDA Nod Is Narrower Than Expected
- Source: drugdu
- 117
- November 20, 2023
-
Roche’s subcutaneous Tecentriq recommended by CHMP for multiple cancer types
- Source: drugdu
- 171
- November 18, 2023
-
Merck’s Keytruda wins coveted FDA nod around surgery for early lung cancer—with a surprise
- Source: drugdu
- 172
- October 19, 2023
-
More walkable neighborhoods have a lower incidence of obesity-related cancers among women
- Source: drugdu
- 124
- October 9, 2023
-
NICE recommends more genetic testing for links to ovarian cancer
- Source: drugdu
- 103
- September 30, 2023
-
Astellas Strikes Another Deal to Expand in Cancer, Partnering With PeptiDream
- Source: drugdu
- 115
- July 27, 2023
-
Merck’s Keytruda, Novartis’ Kisqali face their moment of truth in early-stage cancers
- Source: drugdu
- 118
- May 30, 2023
-
With Novartis circling, Lilly touts Verzenio’s ability to help cancer patients make memories in TV ad
- Source: drugdu
- 125
- May 27, 2023
-
Quest Expands in Cancer Testing With $300M Haystack Oncology Acquisition
- Source: drugdu
- 175
- April 29, 2023
your submission has already been received.
OK
Subscribe
Please enter a valid Email address!
Submit
The most relevant industry news & insight will be sent to you every two weeks.