-
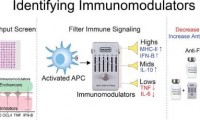
Immunomodulators boost vaccine response and reduce inflammation, finds study
- Source: drugdu
- 144
- April 6, 2023
-
A Testosterone Patch Is Being Developed For Menopausal Women—And It Could Be A World First
- Source: drugdu
- 195
- April 4, 2023
-
prioritizing efficacy when considering quality of life
- Source: drugdu
- 226
- March 30, 2023
-
new research New data suggests ‘huge overuse of antibiotics’
- Source: drugdu
- 120
- March 27, 2023
-
Roche Holding AG Receives FDA Approval for New Cancer Treatment
- Source: drugdu
- 140
- March 24, 2023
-
FDA Approves New Drug to Treat Parkinson’s Disease, Providing Hope for Millions of Patients
- Source: drugdu
- 119
- March 24, 2023
-
FDA Grants Breakthrough Therapy Designation to Pfizer’s Investigational Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment
- Source: drugdu
- 238
- March 22, 2023
-
FDA Approves New Drug to Treat Migraine
- Source: drugdu
- 125
- March 22, 2023
-
Novartis Receives FDA Approval for New Heart Failure Drug
- Source: drugdu
- 247
- March 22, 2023
-
FDA Approves New Treatment for Rare Genetic Disorder
- Source: drugdu
- 118
- March 22, 2023
your submission has already been received.
OK
Subscribe
Please enter a valid Email address!
Submit
The most relevant industry news & insight will be sent to you every two weeks.