Zai Lab’s Phase III clinical trial of this drug achieved positive results
July 3, 2025
Source: drugdu
 156
156
On June 30, Zai Lab announced that the main data of the Phase III study of bemazumab for FGFR2b-positive first-line gastric cancer achieved positive results . Zai Lab said that the detailed results of the study will be announced at a future medical conference, but this achievement is expected to redefine the standard treatment of first-line gastric cancer and bring new hope of survival to gastric cancer patients.
01 New breakthrough
The FORTITUDE-101 study is a global multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial designed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of bematuzumab combined with mFOLFOX6 chemotherapy versus placebo combined with mFOLFOX6 as first-line treatment. The study was conducted in 300 research centers in 37 countries around the world, with a total of 547 patients enrolled.
The study met its primary endpoint of overall survival (OS) at a pre-specified interim analysis, with bematumab plus chemotherapy demonstrating a statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in OS compared with placebo plus chemotherapy, making it the first and only FGFR2b inhibitor to show an OS benefit.
The success of Phase 3 clinical studies is often a key step for drugs to enter the market and benefit patients. This breakthrough of Bematumab means that it is expected to become a new standard for first-line gastric cancer treatment, changing the existing treatment landscape and allowing more patients to benefit from this innovative therapy.
Gastric cancer is one of the most harmful malignant tumors in the world, and its severity can be seen from relevant data. According to authoritative statistics, gastric cancer is the fifth leading cause of cancer-related deaths in the world, with nearly 1 million new cases and more than 650,000 deaths each year. In China, the incidence of gastric cancer is even more severe, with more than 360,000 new cases each year, accounting for about 40% of the world. This means that almost one in every three new gastric cancer patients is from China, and China faces huge challenges in the prevention and treatment of gastric cancer.
What is even more worrying is that the prognosis of gastric cancer is not optimistic. Since the early symptoms of gastric cancer are often not obvious, most patients are already in the advanced stage when diagnosed. Data show that 80% of patients in China are diagnosed in the advanced or metastatic stage, and for stage IV patients, the 5-year survival rate is less than 10%. This low survival rate highlights the huge unmet medical needs in the field of gastric cancer treatment.
Currently, HER2+ targeted therapy and immunotherapy have changed the first-line treatment pattern of advanced gastric cancer to a certain extent, and the survival of patients has gradually improved. However, these two treatment methods have not yet broken through the 2-year survival bottleneck, and the long-term survival of patients is still facing challenges.
In this context, the emergence of Bematuzumab is timely. Studies have found that 38% of patients with advanced gastric cancer/gastroesophageal junction cancer have overexpression of FGFR2b, and about 16% have overexpression of FGFR2b ≥10%. As a Fc segment-modified specific IgG1 antibody targeting the FGFR2b receptor, Bematuzumab exerts anti-tumor effects through a dual mechanism of action, bringing new treatment options and hope to gastric cancer patients with overexpression of FGFR2b.
It is worth mentioning that there is currently no approved treatment specifically for FGFR2b overexpression in gastric cancer in China. Zai Lab's Bemazumab is expected to become the first in China.
02 The advantages of precision treatment are highlighted
Although the specific results of the Phase 3 study have not yet been announced, a review of the data from the Phase 2 FIGHT study is enough to give us a glimpse into the potential of bemazumab. The results of the Phase 2 FIGHT study showed that bemazumab combined with chemotherapy can significantly prolong the survival of patients with FGFR2b-overexpressing gastric cancer , and the higher the proportion of FGFR2b-overexpressing cells, the better the efficacy.
This result reveals the advantages of bemazumab's precision therapy, which can accurately target cancer cells that overexpress FGFR2b and exert a powerful anti-tumor effect. At the same time, the positive correlation between this efficacy and the degree of FGFR2b overexpression further clarifies its mechanism of action and applicable population, providing a clear direction for subsequent clinical applications and research.
In addition, in the Asian population, Bemazumab showed a more significant therapeutic effect. This feature is of great significance because the incidence of gastric cancer is high in Asia, especially in East Asia, and FGFR2b overexpression is more prominent in Asian gastric cancer patients. FGFR2b overexpression has a poor prognosis, resulting in short survival of patients. Therefore, the median OS (overall survival) of Bemazumab in the Phase 2 study can even reach 30 months, a number that can be called "shocking" in the field of gastric cancer treatment. For patients with advanced gastric cancer, it is rare to achieve such a long survival period.
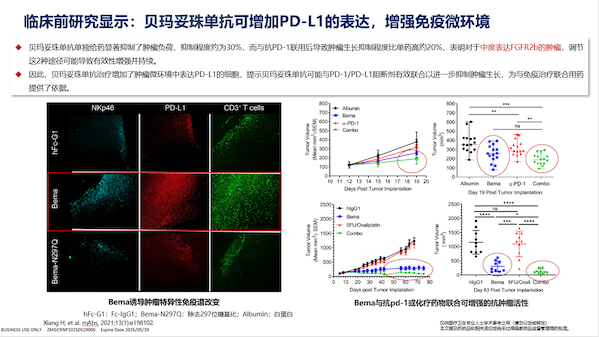
Preclinical studies have provided more possibilities for the application of bemazumab. Studies have shown that bemazumab can increase the expression of PD-L1, thereby enhancing the immune microenvironment. Based on this finding, FORTITUDE-102, a global multicenter clinical study of bemazumab combined with chemotherapy and immunotherapy, is currently underway and has completed enrollment. The results of the study are expected to be read out this year.
03 R&D in multiple areas
In addition to Bematuzumab, Zai Lab has achieved several important results in the field of R&D in the first half of 2025, demonstrating its strong R&D strength and innovation capabilities.
ZL-1310 released updated data for SCLC (small cell lung cancer) at ASCO (American Society of Clinical Oncology), showing strong anti-tumor activity and safety. This result shows that Zai Lab's in-depth exploration and research in the field of small cell lung cancer treatment has achieved remarkable results, bringing new treatment hope to patients with small cell lung cancer.
Zai Lab's self-developed IL-13/IL-31R dual antibody ZL-1503 also brought good news in the treatment of atopic dermatitis. The release of new preclinical data laid the foundation for its further development and clinical application. Atopic dermatitis is a common chronic, recurrent inflammatory skin disease that seriously affects the quality of life of patients. The development of ZL-1503 is expected to provide a new and more effective treatment option for patients with atopic dermatitis, meeting unmet clinical needs.
In addition, at the AACR (American Association for Cancer Research) annual meeting, Zai Lab announced research data on two new-generation anti-tumor drug candidates developed internally (ZL-6201 and ZL-1222) :
ZL-6201 is able to efficiently internalize and kill tumor cells, while also exhibiting a strong bystander killing effect in the tumor microenvironment where LRRC15 is overexpressed. Multiple in vitro and in vivo preclinical studies have shown that ZL-6201 treatment can effectively inhibit the growth of established tumors.
ZL-1222 precisely regulates IL-12 activity and PD-1 targeting, demonstrating potent anti-tumor activity in both anti-PD-1 antibody-sensitive and anti-PD-1 antibody-resistant tumor models, and has higher systemic safety.
These achievements not only demonstrate Zai Lab's profound strength and rich reserves in the field of innovative drug research and development, but also reflect its continuous exploration and innovation, and its commitment to providing patients with more treatment options and hope.
https://news.yaozh.com/archive/45710.html
By editorRead more on
- Rovaxitinib approved for marketing, filling the demand for myelofibrosis treatment March 2, 2026
- Warrant Pharmaceuticals’ active pharmaceutical ingredient receives Brazil’s first official GMP certification March 2, 2026
- Merck’s New Story March 2, 2026
- Rongchang Biotechnology has turned a profit! March 2, 2026
- Jiuyuan Gene’s “Simeglucopyranoside” for weight loss (Jikeqin®) has been submitted for market approval March 2, 2026
your submission has already been received.
OK
Subscribe
Please enter a valid Email address!
Submit
The most relevant industry news & insight will be sent to you every two weeks.



