Lepu Biopharmaceuticals’ combination therapy enters Europe
July 2, 2025
Source: drugdu
 214
214
Recently, Lepu Bio announced that its application for a Phase II clinical trial of its investigational EGFR-targeted ADC MRG003 combined with the PD-1 monoclonal antibody Putelizumab versus monotherapy for the treatment of locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma has been approved by the European Medicines Agency, and enrollment is scheduled to start in the third quarter of 2025.
It is reported that this study is the world's first clinical study of EGFR ADC combined with PD-1 monoclonal antibody in locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.
The world's first
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma is a type of malignant tumor with significant heterogeneity and a high tendency to recur and metastasize. About 60% of patients have progressed to the locally advanced or metastatic stage when diagnosed, and the overall 5-year survival rate is only 30%-50%. In 2022, there will be 145,000 new cases of head and neck malignant tumors in China, and the incidence rate is increasing year by year. In the field of recurrent/metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, the survival benefits of traditional chemotherapy and targeted therapy have always been limited, and the median overall survival of advanced first-line treatment has long failed to exceed 1 year.
Currently, cetuximab, chemotherapy, and PD-1 monoclonal antibodies commonly used in clinical practice in China all have obvious limitations. For example, although cetuximab combined with chemotherapy is a standard regimen, some patients may experience severe adverse reactions such as gastrointestinal toxicity and mucositis; although PD-1 inhibitor monotherapy improves overall survival and duration of remission in PD-L1-positive patients, it does not significantly improve progression-free survival and overall remission rate, and better treatment options are urgently needed in the clinic.
MRG003 is an ADC targeting EGFR. It achieves precise killing of EGFR-high-expressing tumor cells through the innovative design of high-affinity EGFR antibody (affinity increased 6-7 times compared with cetuximab), cleavable vc linker and potent toxin MMAE. The Phase I/II study data released at the 2024 ASCO Annual Meeting showed that MRG003 combined with putelimab had an objective response rate (ORR) of 60% and a disease control rate (DCR) of 80% in 5 evaluable first-line head and neck cancer patients, initially demonstrating the synergistic advantages of combined therapy.
In a simple comparison with approved drugs, Merck's pembrolizumab (K drug) achieved an ORR of 37% in the total population in the Phase III KEYNOTE-048 study when combined with chemotherapy. Although the current clinical sample size of MRG003 is limited, the initial data of MRG003 combined with PD-1 monoclonal antibody has shown significant advantages, suggesting iterative potential.
MRG003 combined with Putelimab has been approved by the European Union to start a Phase II clinical study, focusing on patients with locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, exploring the value of the "ADC+IO" combination regimen in early intervention of the disease. This study innovatively moved the treatment window forward to before the first-line treatment of the late stage, and by optimizing the treatment strategy, prolonged the patient's survival and improved the quality of life. It became the world's first clinical exploration of EGFR ADC combined with PD-1 monoclonal antibody in advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, and is expected to reshape the treatment landscape in this field.
For nasopharyngeal carcinoma, MRG003 is already in the domestic market review stage and is expected to become the first EGFR ADC drug approved in China. At the same time, MRG003 has been granted breakthrough therapy certification by the FDA for its indication for recurrent/metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
At the 2025 ASCO Annual Meeting, Lepu Biopharma disclosed for the first time the Phase IIb data of MRG003 for the treatment of advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma. The results showed that the ORR of the MRG003 group evaluated by BICR reached 30.2% (11.5% in the chemotherapy group), the median progression-free survival (PFS) increased to 5.8 months, and the updated median overall survival (OS) reached 17.1 months. This study is the first randomized controlled study to evaluate the use of EGFR ADC versus chemotherapy in patients with recurrent/metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma, and it showed clinically significant ORR, PFS and OS benefits, while having good safety.
Differentiated layout
Lepu Bio's layout in the ADC field goes far beyond MRG003. The company has built a rich and differentiated ADC pipeline, forming a clinical development pattern with multiple targets and multiple cancer types.
MRG002 is a HER2-targeted ADC that is being studied for indications such as breast cancer, urothelial carcinoma, and gastric cancer/gastroesophageal junction cancer with high HER2 expression.
MRG004A targets tissue factor (TF) and has shown anti-tumor activity in pancreatic cancer, triple-negative breast cancer, and cervical cancer. In March 2024, it was recognized as a breakthrough therapy by the FDA for the treatment of recurrent or refractory pancreatic cancer. Phase I data as of December 2023 showed that the 2.0 mg/kg dose group had an ORR of 33.3% and a DCR of 83.3% in pancreatic cancer patients; especially in patients with TF expression ≥50% and ≤2 previous lines of treatment, the ORR and DCR were as high as 80% and 100%, respectively, and the median progression-free survival was 5.5 months.
MRG001 is a CD20-targeted ADC for patients with B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma who have primary or acquired resistance to rituximab. Currently, a Phase Ib dose expansion study in China has observed good preliminary efficacy in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
MRG006A is a topoisomerase I inhibitor ADC targeting GPC-3 developed based on the Hi-TOPi platform. It received IND approval from the National Medical Products Administration in July 2024 and started Phase I clinical trials. Preclinical studies have shown that it exhibits a dose-dependent tumor growth inhibitory effect in liver cancer PDX models, and toxicology studies have also confirmed good safety.
CMG901 is a CLDN18.2-targeted ADC, which consists of a specific antibody, a cleavable linker and an MMAE payload. It is clinically explored for solid tumors such as Claudin18.2-positive gastric cancer and pancreatic cancer. CMG901 is the first CLDN18.2-targeted ADC approved for IND in China and the United States.
Most ADC drugs have been approved for marketing at an accelerated pace based on single-drug/single-arm clinical research data in terminal patients. However, how to expand indications and allow more patients to benefit on the front line of treatment has become a key issue that the industry urgently needs to break through. More and more clinical evidence shows that ADC drugs are sensitive to the efficacy of immunotherapy drugs, so the combined use of the two has become an important trend in current clinical practice.
ADC and IO drugs have strong synergistic effects in terms of their mechanism of action, and there are no overlapping adverse reactions. This lays a theoretical basis for the future treatment of PD-1 monoclonal antibodies combined with different types of ADC drugs in first-line treatment and later-line treatment.
Lepu Biopharma has advanced 6 ADC pipelines to the clinical stage. The company will combine its two fastest-progressing ADC products, MRG003 and MRG002, with its already-marketed PD-1 monoclonal antibody Putelizumab to fully explore new opportunities for "IO+ADC" combination therapy.
MRG002+putelimab: Phase II trials for the treatment of HER2-expressing solid tumors have been completed, and good data have been observed in the treatment of urothelial carcinoma. The results showed that as of April 2024, the ORR of all evaluated patients reached 64.0%, and the DCR reached 89.0%; the ORR and DCR of the 1.8 mg/kg dose group were 70.0% and 90.0%, respectively; the ORR of the HER2-positive patient subgroup was as high as 70.6%, and the DCR reached 94.1%. The longest PFS of the treated patients exceeded 26.5 months and continued to remit, which preliminarily verified the synergistic advantages of the combination regimen.
CMG901+putlimab: A Phase Ib/II study for Claudin18.2-positive gastric cancer is underway, and preclinical data show significant synergistic effects.
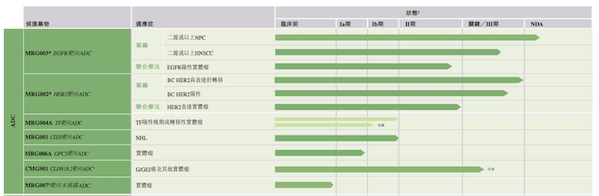 Lepu Biopharmaceuticals’ ADC pipeline layout
Lepu Biopharmaceuticals’ ADC pipeline layout
Image source: Lepu Biotech
Competitive Landscape
In 2023, there will be 2.17 million new cases of non-small cell lung cancer worldwide. EGFR mutation is a key driver gene, with a mutation rate of over 50% in Asians, significantly higher than the 10% rate in Westerners. There are approximately 700,000 new EGFR mutation NSCLC patients worldwide each year, making this target the core direction of precision medicine.
According to current clinical guidelines in China and the United States, the first-line treatment for EGFR mutant NSCLC is mainly based on tyrosine kinase inhibitors such as afatinib, erlotinib, and osimertinib. However, most patients will develop drug resistance 9-14 months after treatment, and more effective follow-up treatment options are urgently needed.
In response to the drug resistance dilemma, clinical exploration is mainly focused on four major directions: strengthening target inhibition through EGFR dual antibodies or combined drug use, using immune checkpoint inhibitors combined with chemotherapy, developing a highly selective new generation of EGFR inhibitors, and using ADC to achieve precise killing of tumor cells. Among them, EGFR ADC has become a research and development hotspot in recent years due to its mechanism of "antibody targeted delivery + toxin precise killing".
Currently, the only EGFR ADC approved in the world is Rakuten Medical's Cetuximab saratolacan, which is used to treat head and neck cancer. Its unique photodynamic therapy mode requires daily intravenous injection of drugs and then irradiation of the lesion for 20-28 hours with a patented laser device. Although it has set a precedent for the clinical application of EGFR ADC, the complex treatment process limits its popularity.
In the R&D pipeline, Lepu Bio's MRG003 has been submitted for marketing approval for nasopharyngeal carcinoma and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, and is expected to become the first EGFR ADC in China.
As an EGFR×HER3 dual-target ADC, Baili Tianheng's BLB01D1 is conducting Phase III clinical trials to explore indications such as nasopharyngeal carcinoma and non-small cell lung cancer.
In addition, Innovent Biologics, AstraZeneca, CSPC Pharmaceuticals, and Henlius Biopharmaceuticals are all developing EGFR ADC drugs.
SYS6010 is an EGFR ADC independently developed by Jushi Bio (a subsidiary of CSPC Pharmaceuticals). It binds to EGFR on the surface of tumor cells through antibodies, releases the topoisomerase I inhibitor JS-1 through endocytosis, induces DNA damage and triggers cell apoptosis, and kills surrounding tumor tissues through the "bystander effect". Currently, the drug is in key Phase III clinical trials for NSCLC patients who have failed EGFR TKIs treatment, and is also being used in multiple cancers such as breast cancer and esophageal cancer.
Phase I study data disclosed at the 2025 AACR conference showed that in an analysis of 269 patients with solid tumors (including 164 NSCLC patients, with a median of 3 lines of treatment), the ORR of 224 evaluable patients was 31.3%, and the DCR reached 85.3%; the ORR of the 4.8 mg/kg dose group increased to 37.5%. Among 102 patients with EGFR-mutated non-squamous NSCLC, the ORR reached 39.2% and the DCR reached 93.1%. Among them, the ORR of patients with simple EGFR-TKI resistance was as high as 63.2%, and the ORR of patients with dual resistance (EGFR-TKI + platinum-containing chemotherapy) was still 33.3%, showing significant efficacy in multidrug-resistant populations.
Conclusion
The Phase II clinical trial of MRG003 combined with putelizumab for the treatment of locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma has been approved by the European Medicines Agency. As the world's first clinical study on the combination of EGFR ADC and PD-1 monoclonal antibody in the field of locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, this trial relies on differentiated R&D strategies and international layout advantages, focuses on unmet clinical needs, and explores innovative models of "ADC+IO" combination therapy by building a synergistic pipeline combination.
EGFR-targeted ADC drugs can achieve precise killing of tumor cells through antibody-mediated therapy and combined with the immunomodulatory effect of PD-1 monoclonal antibodies to form a synergistic effect of "precision killing + immune activation", and are expected to become a new treatment option with both efficacy and safety.
https://news.yaozh.com/archive/45699.html
By editorRead more on
- Rovaxitinib approved for marketing, filling the demand for myelofibrosis treatment March 2, 2026
- Warrant Pharmaceuticals’ active pharmaceutical ingredient receives Brazil’s first official GMP certification March 2, 2026
- Merck’s New Story March 2, 2026
- Rongchang Biotechnology has turned a profit! March 2, 2026
- Jiuyuan Gene’s “Simeglucopyranoside” for weight loss (Jikeqin®) has been submitted for market approval March 2, 2026
your submission has already been received.
OK
Subscribe
Please enter a valid Email address!
Submit
The most relevant industry news & insight will be sent to you every two weeks.



