China leads the world in developing the fourth druggable immune checkpoint drug
June 3, 2025
Source: drugdu
 166
166
The 2025 American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting is in full swing, and the original innovative drug LBL-024 from China has once again become the focus.
The drug is a 4-1BB/PD-L1 bispecific antibody that is expected to fill the gap in the clinical treatment of extrapulmonary neuroendocrine carcinoma (EP-NEC). At the same time, positive efficacy signals have been observed in multiple cancer types such as small cell lung cancer and biliary tract cancer.
It is worth noting that LBL-024 has entered the critical clinical trial stage. If approved, it will become the world's first 4-1BB target drug, and will also make 4-1BB the world's fourth druggable immune checkpoint after PD-1/L1, CTLA-4, and LAG3.
01 The world's first! LBL-024 breaks through again
The American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting is the world's largest, most academically advanced and most authoritative clinical oncology conference, and the selected oral reports must be the most representative research in the field of cancer.
LBL-024 has been included in ASCO oral presentations for two consecutive years.
At the 2024 ASCO conference, Wei Lizhibo reported the significant efficacy and safety advantages of LBL-024 in the second-line treatment of advanced extrapulmonary neuroendocrine carcinoma (EP-NEC). Its Phase I/IIa single-drug efficacy data showed that at a dose of 15 mg/kg, the objective response rate (ORR) of second-line treatment of EP-NEC was 37.5%, and the disease control rate (DCR) was 50.0%. This shows that LBL-024 is expected to become the first approved standard treatment for EP-NEC after progression of the second-line treatment.
At this year's ASCO conference, Wellizbo disclosed the breakthrough clinical data of LBL-024 in the first-line treatment of advanced EP-NEC: the combination with chemotherapy was well tolerated, and the efficacy was significantly better than the historical data of chemotherapy alone (ORR of about 30%-55%). This marks that the indication boundary of LBL-024 has been expanded from late-line treatment to earlier treatment stages.
This is a multicenter Phase Ib/II trial. As of April 15, 2025, a total of 55 patients were included, including 15 patients in Phase Ib (12 EP-NEC patients, 2 SCLC patients, and 1 MiNEN patient) and 40 patients in Phase II (all EP-NEC patients). The results showed:
Among the 52 patients evaluable for efficacy, the overall ORR was 75.0% (39/52 ) and the DCR was 92.3% (48/52).
Phase II 15 mg/kg group: ORR was 83.3% (15/18) , DCR was 100% (18/18).
Subgroup analysis showed that the ORRs of patients with genitourinary system NEC, pancreatic NEC, SCLC, and esophageal NEC were 100.0%, 83.3%, 100.0%, and 77.8%, respectively.
In terms of safety, the incidence of AEs in the 26 patients treated with a 15 mg/kg dose was comparable to that of patients treated with a 6 mg/kg dose. Most TEAEs were mild to moderate in severity (grade 1-2), and no unexpected safety signals were found. The most common TEAEs were hematologic toxicity and nausea related to EP/EC chemotherapy.
Neuroendocrine carcinoma (NEC) is a highly malignant tumor, which is divided into lung NEC and EP-NEC. EP-NEC is a rare and highly invasive cancer. The prognosis of advanced EP-NEC is extremely poor. The first-line standard treatment is etoposide/platinum chemotherapy, but there is a lack of second-line and subsequent standard treatments. There is a high unmet clinical need, and new treatment options are urgently needed.
Based on the current treatment status of EP-NEC and the superior safety and efficacy data of LBL-024, LBL-024 was approved by NMPA on April 30, 2024 to conduct a single-arm pivotal registration clinical study, and is expected to become the first approved drug for the treatment of extrapulmonary neuroendocrine cancer.
In addition, LBL-024 received Breakthrough Therapy Designation (BTD) from the NMPA for the treatment of post-line extrapulmonary neuroendocrine carcinoma in October 2024, and received Orphan Drug Designation (ODD) from the FDA for LBL-024 for the treatment of neuroendocrine carcinoma in November 2024 , which will also speed up the regulatory approval of the drug. Virbac expects to submit a BLA in 2026 and obtain conditional approval in 2027.
02 Expansion of multi-cancer treatment landscape
4-1BB (CD137) is an immune checkpoint molecule that has attracted much attention in recent years. Its mechanism is to activate T cells and natural killer cells (NK cells) to enhance anti-tumor immune response. Different from the "de-inhibition" strategy of targets such as PD-1/L1, 4-1BB "positively activates" immune cells, providing a new possibility for tumor treatment, which currently uses PD-1/PD-L1 as the main pathway but has an overall efficacy of only about 20%.
If the human immune system is compared to a car, T cells are the "core engine" against cancer cells. In this process, inhibitors such as PD-1 and CTLA-4 are like releasing the brakes, eliminating the inhibitory effect of tumors on T cells and restoring the engine's power; while 4-1BB agonists are like stepping on the accelerator directly, causing T cells to enter an overclocked state through costimulatory signals, resulting in a stronger burst of lethality. This provides new hope for the treatment of some so-called "cold tumors" and PD-1/PD-L1-resistant tumors.
However, due to the widespread expression of 4-1BB, it carries the potential risk of liver toxicity and systemic immune response, while the efficacy of treatment at a safe dose is limited. Therefore, the early development process of 4-1BB agonists was not smooth.
To meet these challenges, Wellizbo developed a 4-1BB and PD-L1 dual-targeting bispecific antibody, LBL-024, based on its original X-body™ technology platform . It features a 2:2 structural design, with two binding domains for PD-L1 and 4-1BB respectively, and the binding affinity of PD-L1 and 4-1BB is significantly different, making the interaction with PD-L1 stronger than that with 4-1BB.
This unique molecular design, on the one hand, enhances the specificity of 4-1BB activation by limiting co-stimulation and subsequent immune activation to the tumor environment expressing PD-L1; on the other hand, local and conditional activation of 4-1BB greatly reduces the risk of organ system toxicity such as hepatotoxicity, thereby expanding the therapeutic window.
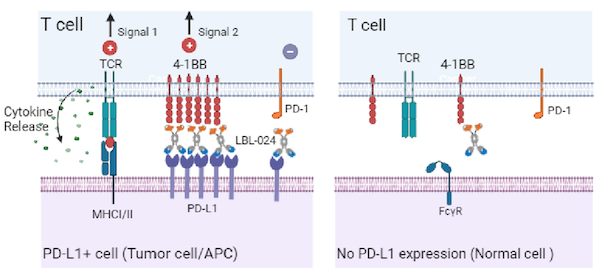 Figure 1 Mechanism of action of LBL-024
Figure 1 Mechanism of action of LBL-024
Image source: Wei Li Zhibo
Currently, LBL-024 has entered the key registration clinical research stage for extrapulmonary neuroendocrine cancer. There is no 4-1BB target drug on the market in the world, and LBL-024 is expected to become the first.
It is worth noting that 4-1BB is widely expressed and has the potential to treat a broad spectrum of cancers comparable to PD-1/L1 inhibitors. According to Frost & Sullivan data, the total number of cases for the main indications of 4-1BB antibodies has increased year by year, from 9.717 million cases in 2016 to 10.634 million cases in 2020, and the market prospects are broad.
Extrapulmonary neuroendocrine cancer is only the first stop for LBL-024. WellZhibo is also exploring its therapeutic effects on more cancer types, including small cell lung cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, biliary tract cancer, ovarian cancer, esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, liver cancer, gastric cancer and other major cancers, and has shown preliminary efficacy signals.
Small cell lung cancer
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is also a neuroendocrine cancer, accounting for 15% of all lung cancer cases, and is characterized by rapid progression, strong metastasis, and high mortality. In recent years, the combination of PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors and chemotherapy has been recommended for the first-line and late-stage treatment of diffuse small cell lung cancer. However, most patients will develop primary resistance to current therapies, or quickly develop acquired resistance, and there are very few drugs approved for effective second-line treatment of small cell lung cancer.
4-1BB/PD-L1 dual antibody provides a new solution for the treatment of small cell lung cancer.
LBL-024 combined with etoposide and platinum chemotherapy showed good safety and preliminary efficacy in the first-line clinical phase Ib/II of small cell lung cancer. As of February 14, 2025, among 19 evaluable patients, the ORR was 84.2% (16/19) and the DCR was 100%.
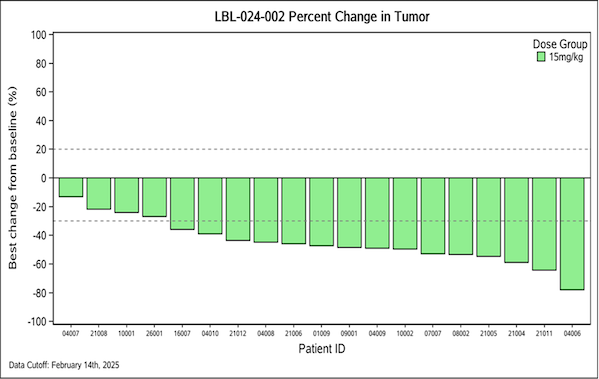 Figure 2. Percent change in tumor size after treatment with LBL-024-002 (as of February 14, 2025)
Figure 2. Percent change in tumor size after treatment with LBL-024-002 (as of February 14, 2025)
Image source: Wei Li Zhibo
Biliary tract cancer
Biliary tract cancer (BTC) is a common digestive tract tumor, accounting for about 3% of adult cancers worldwide, and its incidence has been on the rise in recent years.
Currently, there are limited treatment options for biliary tract cancer, with most patients presenting with locally advanced or metastatic disease. Although monospecific antibodies targeting PD-L1 have demonstrated durable clinical benefits and long-term responses, their effectiveness is limited to a small subset of patients who respond positively to PD-L1 inhibitors.
Recent research progress has shown that bispecific antibodies such as PD-L1/4-1BB can simultaneously bind to co-inhibitory molecules and co-stimulatory molecules, thereby enhancing sustained anti-tumor responses.
Phase I/II trial data of LBL-024 monotherapy showed that as of September 30, 2024, among 25 evaluable patients with biliary tract cancer, 1 achieved complete remission (remission duration up to 100 weeks), 1 achieved partial remission, and 11 achieved stable disease, with ORR and DCR of 8.0% and 52.0%, respectively.
Other cancers
LBL-024 has been approved for Phase II clinical studies for indications such as non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), ovarian cancer (OC), esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC), liver cancer (HCC) and gastric cancer, and we look forward to more clinical data.
03 Three major platforms to build global competitiveness
Since the advent of the PD-1 monoclonal antibody K and O in 2014, tumor immunotherapy (IO) has become a sharp weapon for the first-line treatment of many advanced tumors, and K has successfully become the "king of medicine". However, these immunotherapies currently on the market are only effective for about 20% of patients. At present, the IO track has quietly entered the 2.0 era.
WellZhibo is one of the best. Since its establishment, the company has been committed to the discovery, development and commercialization of innovative therapies to meet the unmet medical needs in tumors, autoimmune diseases and other major diseases in China and the world.
At present, Wellizbo has established three core technology platforms, LeadsBody™ platform (CD3 T-Cell Engager platform), X-body™ platform (4-1BB Engager platform) and ADC platform. The company currently has 12 innovative drug candidates, 6 of which have successfully entered the clinical stage.
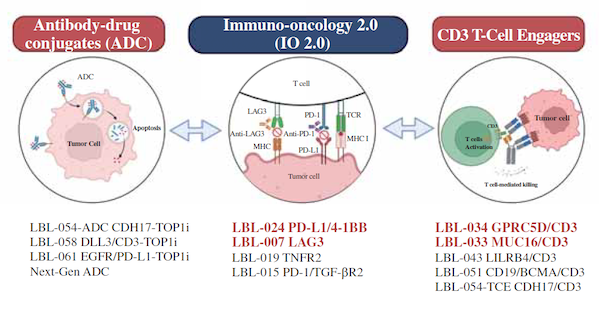 Figure 3 Virbac's drug candidates
Figure 3 Virbac's drug candidates
Image source: Weilizhibo prospectus
Conclusion
From Wellizbo's R&D pipeline, we can see its determination to insist on true innovation and to bravely enter new territory.
At present, the company has built a number of innovative technology platforms and has produced a number of candidate drugs with FIC and BIC potential. Among them, the first pipeline LBL-024 is expected to become the world's first marketed 4-1BB targeted drug, and the first truly original Chinese tumor immunotherapy drug. Moreover, the broad-spectrum characteristics of cross-tumor treatment indicate huge clinical potential and commercial value. In the subsequent pipeline echelons, the research and development progress of multiple TCE bispecific antibodies and next-generation ADCs ranks among the top in the world, fully confirming the innovative leadership of Virbac in the field of next-generation tumor immunotherapy.
https://news.yaozh.com/archive/45559.html
By editorRead more on
- Rovaxitinib approved for marketing, filling the demand for myelofibrosis treatment March 2, 2026
- Warrant Pharmaceuticals’ active pharmaceutical ingredient receives Brazil’s first official GMP certification March 2, 2026
- Merck’s New Story March 2, 2026
- Rongchang Biotechnology has turned a profit! March 2, 2026
- Jiuyuan Gene’s “Simeglucopyranoside” for weight loss (Jikeqin®) has been submitted for market approval March 2, 2026
your submission has already been received.
OK
Subscribe
Please enter a valid Email address!
Submit
The most relevant industry news & insight will be sent to you every two weeks.



