Now is the best time for influenza vaccination
January 10, 2025
Source: drugdu
 364
364
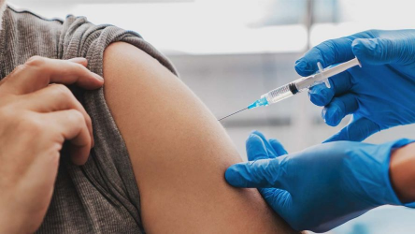 Recently, China CDC released the latest national sentinel surveillance of acute respiratory infectious diseases. The analysis of the monitoring results shows that, at present, acute respiratory infectious diseases are generally showing a continuous upward trend, and the trends of infection caused by different pathogens are different. Influenza is generally in the seasonal epidemic period, and the positive rate of influenza virus is rising rapidly; among them, the positive rate of influenza virus in outpatient and emergency influenza-like cases nationwide has increased by 6.2% compared with last week.
Recently, China CDC released the latest national sentinel surveillance of acute respiratory infectious diseases. The analysis of the monitoring results shows that, at present, acute respiratory infectious diseases are generally showing a continuous upward trend, and the trends of infection caused by different pathogens are different. Influenza is generally in the seasonal epidemic period, and the positive rate of influenza virus is rising rapidly; among them, the positive rate of influenza virus in outpatient and emergency influenza-like cases nationwide has increased by 6.2% compared with last week.
The positive pathogens detected in the outpatient and emergency departments of sentinel hospitals are mainly influenza virus, human metapneumovirus, and rhinovirus, and the positive pathogens detected in hospitalized severe acute respiratory infection cases are mainly influenza virus, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and human metapneumovirus. In other words, influenza is one of the most important pathogens in both outpatient and emergency cases and inpatient severe cases.
In addition, there are differences in the test results between the north and the south and between people of different age groups. The level of influenza activity varies between different provinces, and the increase in northern provinces is slightly obvious, but it is still lower than the same period last year. The positive rate of respiratory syncytial virus in cases aged 0-4 years, and the positive rate of human metapneumovirus in cases aged 14 years and below showed a fluctuating upward trend, with a more obvious upward trend in northern provinces. The positive rate of Mycoplasma pneumoniae in northern provinces continued to decline, while Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in southern provinces remained at a low level. The positive rate of rhinovirus continued to decline nationwide, and the positive rate of adenovirus showed a fluctuating downward trend.
According to the China Center for Disease Control and Prevention, influenza, also known as influenza, is an acute respiratory infectious disease caused by influenza virus, which usually causes many people to be infected in a certain season or time period, and has obvious seasonality. According to the World Health Organization, seasonal epidemics of influenza viruses can cause an average of about 3 million to 5 million severe cases and 290,000 to 650,000 respiratory disease-related deaths each year worldwide.
Although influenza and the common cold are both respiratory diseases, they are completely different. The pathogen of influenza is influenza virus, while the common cold is caused by rhinovirus, parainfluenza virus, common coronavirus, etc. In contrast, influenza is highly contagious and has obvious seasonality. Patients often experience high temperatures of 39℃-40℃, accompanied by headaches, fatigue, body muscle aches, chills, etc., and the course of the disease is about 7-10 days; while the common cold usually does not cause fever or has mild to moderate fever, and its symptoms are mainly reflected in obvious upper respiratory tract symptoms, such as runny nose, sneezing, nasal congestion, sore throat, etc., and the course of the disease is usually 3-5 days.
Why are respiratory infectious diseases prone to high incidence in autumn and winter and winter and spring? It points out that the reasons mainly include the following aspects: First, the cold season is more conducive to the survival of most pathogens. Second, doors and windows are often closed in autumn and winter and spring, and indoor air circulation is reduced. Once there is an infectious source, it is easy to cause disease transmission. Third, the resistance of the nasal mucosa decreases in the cold season, and pathogens are more likely to invade the human body. Fourth, there are many indoor activities in the cold season, which increases the chance of infection.
What is the current epidemic situation? Kan Biao, director of the Institute of Infectious Diseases of the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, said that judging from the current situation, the scale and intensity of respiratory infectious diseases this year are lower than last year, and it is expected that this winter and next spring will still show a trend of alternating or overlapping epidemics of multiple respiratory infectious diseases.
So, how to prevent multiple respiratory infectious diseases? The Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention emphasized that vaccination is the most economical and effective way to prevent infectious diseases. It is currently the best time for influenza vaccination. All people aged 6 months and above who have no contraindications to vaccination can be vaccinated with influenza vaccine, especially high-risk groups such as the elderly, children, and patients with chronic basic diseases.
In addition, taking daily protection and public health measures can also effectively achieve the prevention of multiple respiratory infectious diseases, including paying attention to cough etiquette and hand hygiene, and developing good hygiene habits; strengthening physical fitness, paying attention to balanced nutrition, improving physical resistance, and developing a healthy lifestyle; trying to avoid crowded public places, especially closed places with poor air circulation; reducing contact with people with respiratory symptoms, and paying attention to personal protection when contacting; and doing a good job of indoor ventilation.
https://news.yaozh.com/archive/44788.html
By editorRead more on
- Gan & Lee Pharmaceuticals’ new PROTAC drug GLR2037 tablets have been approved for clinical trials to enter the field of prostate cancer treatment March 3, 2026
- AideaPharmaceuticals plans to raise no more than 1.277 billion yuan through a private placement to focus on the global clinical development of innovative HIV drugs March 3, 2026
- Giant Exits! Its Star Business Acquired March 3, 2026
- Focusing on cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases! OpenMediLead Medical Intelligence Dual Engines Launch Internal Testing, Connecting Drug Development and Clinical Diagnosis in a Closed Loop March 3, 2026
- Innovent Biologics Announces Approval of New Indication for BTK Inhibitor “Pitubrutinib” in China March 3, 2026
your submission has already been received.
OK
Subscribe
Please enter a valid Email address!
Submit
The most relevant industry news & insight will be sent to you every two weeks.



