AS treatment! TNF-α declines, IL-17 and JAK open new battlefields!
May 15, 2025
Source: drugdu
 223
223
Some diseases can make people look up at the sky forever, while some diseases can also make people look at the ground forever, and this is ankylosing spondylitis.
Regarding the pain points of ankylosing spondylitis (AS), in addition to the spine that is as stiff as if it were poured with cement when you wake up in the morning, this chronic inflammatory disease is like a silent "bone erosion war", spreading from the sacroiliac joints to the spine, and even affecting peripheral joints such as the hip and knee, eventually leaving the patient in the dilemma of "the body gradually becoming petrified."
This "immortal tumor" is even more despairing to the patient's biological quality than most terminal illnesses.
4 million people cannot stand up straight all year round
Strictly speaking, ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a refractory chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease that mainly affects the sacroiliac joints, spine, paraspinal soft tissues and peripheral joints, and may be accompanied by extra-articular manifestations. In severe cases, spinal deformity and ankylosis may occur, with pain and stiffness in the sacroiliac joints and spine as the main symptoms.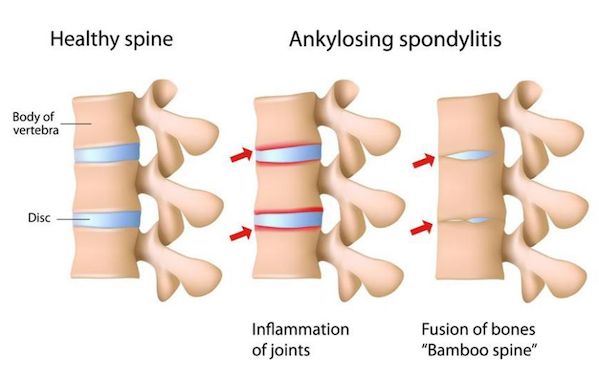 AS is widely distributed around the world, and the prevalence varies greatly between different races and regions. According to current data, the prevalence in China and Italy is significantly higher, with Italy at 0.37% and China at 0.3%. There are about 4 million AS patients in the country, with a male-female ratio of 2:1 to 4:1, and the age of onset is mostly 15 to 40 years old. Therefore, the impact of this disease on our labor force is, in principle, greater than many terminal illnesses.
AS is widely distributed around the world, and the prevalence varies greatly between different races and regions. According to current data, the prevalence in China and Italy is significantly higher, with Italy at 0.37% and China at 0.3%. There are about 4 million AS patients in the country, with a male-female ratio of 2:1 to 4:1, and the age of onset is mostly 15 to 40 years old. Therefore, the impact of this disease on our labor force is, in principle, greater than many terminal illnesses.
AS progresses slowly, has a long course, and there is currently no complete cure, so patients can live with the disease for many years, which has led to the high prevalence and low incidence of AS. It is reported that the incidence of AS is 0.5 to 14/100,000 per year, and the incidence is basically stable.
According to statistics, about two-thirds of patients with ankylosing spondylitis will experience varying degrees of multiple joint lesions throughout the body. Approximately 10%-30% of patients with hip joint involvement will eventually develop varying degrees of bone necrosis[1]. 95% of patients will experience multiple spinal joint lesions and deformities in the lumbar, sacroiliac, thoracic, and cervical vertebrae, with limited ability to bend or squat, difficulty walking, and loss of mobility.
In general, China is a high-incidence area of AS, with a huge potential patient population and treatment market. In addition, the disease has two significant characteristics in its development. The first is the high disability rate. If patients fail to receive timely treatment or receive improper treatment, the three-year disability rate is about 45.5%, and the five-year disability rate is as high as over 70%. The second is the insidious onset of the disease, with atypical early symptoms, leading to missed diagnosis or misdiagnosis as a general low back pain disease. According to statistics, the misdiagnosis rate of ankylosing spondylitis in my country is as high as 70%, with an average misdiagnosis period of 4 years. More than 50% of ankylosing spondylitis patients have already developed to the middle stage when diagnosed.
Therefore, clinically, changing the type of disease is very attractive to new drug research and development companies, whether in terms of treatment willingness, future growth space, or treatment cycle.
According to the forecast of Zhiyan Consulting (see the figure below), from 2014 to 2022, the market size of AS therapeutic drugs in China will increase from 7.064 billion yuan to 11.655 billion yuan, with a compound annual growth rate of 6.2%.
Basic research to promote the improvement of etiology and pathogenesis
AS is a major internationally difficult disease, and its etiology and pathogenesis are still unclear. Currently, the widely recognized pathogenesis of AS includes genetic factors, immune factors, and the influence of the classical osteogenic pathway. These mechanisms are interconnected and together lead to the progression of AS. [2]
Among them, genetic factors are the most important pathogenic factor of AS. Scientists believe that the gene related to AS is human leukocyte antigen B27 (HLA-B27). The positive rate of HLA-B27 in the general population of Asia is only 4%-8%, but the positive rate of HLA-B27 in AS patients is as high as 90%~95%. [3]
Therefore, from a mechanistic point of view, arthritis peptides are presented by HLA-B27 to CD8+T lymphocytes, triggering CD8+T lymphocytes. The incorrect shearing of endoplasmic reticulum aminopeptidase 1/2 (ERAP1/2) will produce abnormal peptides, resulting in the circulation of HLA-B27 free heavy chain and homodimers on the cell membrane. Antigen-presenting cells present HLA-B27 dimers to killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIR) and leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptors. KIR3DL2+CD4+T lymphocytes of AS patients proliferate, activating NK cells and Th17 cells, and increasing IL-17 production. These cells mainly secrete tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interferon-γ (IFN-γ). IL-17 works synergistically with TNF-α or IFN-γ to stimulate the release of inflammatory factors and affect bone structure, thus playing a role in the occurrence and development of AS.
Of course, in addition to HLA-B27, HLA-B07, HLA-B57, HLA-B51, HLA-B47, HLA-B40, HLA-B13 and other HLA-B alleles are also significantly associated with AS susceptibility, and other related HLA molecules may associate AS with other diseases. For example, HLADRB1*0103 is one of the major risk genes for both AS and Crohn's disease, which is consistent with the fact that Crohn's disease patients often suffer from AS.
The era of non-targeted drugs: the multiple limitations of traditional treatments
Currently, there is no cure for AS. The main purpose of treatment is to relieve the patient's symptoms and signs, restore the back and joint function to the greatest extent, and prevent joint damage and systemic complications, thereby improving the patient's quality of life.
Generally speaking, surgery is only used for severe cases, such as joint replacement or spinal correction, but for most AS patients, physical therapy (heat therapy, magnetic therapy, massage, etc.) and drug therapy are the main treatment methods.
In terms of drug treatment of AS, it is currently divided into three main categories: non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, glucocorticoids and anti-rheumatic drugs.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), as the first recommendation in the clinical guidelines for AS, improve symptoms of the spine or peripheral joints by inhibiting cyclooxygenase (COX) activity and reducing prostaglandin synthesis. Common drugs include ibuprofen, diclofenac, acetaminophen, meloxicam, etc. However, in principle, they can only relieve symptoms but cannot prevent bone destruction and disease progression. They also have adverse reactions such as nausea, vomiting, ulcers, and bleeding, as well as adverse reactions such as gastrointestinal adverse reactions and kidney damage.
Glucocorticoids are mainly used to treat extra-articular symptoms such as acute iridocyclitis and have good anti-inflammatory effects. However, their severe systemic side effects (such as osteoporosis and metabolic disorders) limit their long-term use. They have little value in the long-term treatment of AS, and the guidelines explicitly recommend avoiding systemic use.
Anti-rheumatic drugs, such as sulfasalazine and methotrexate, can indeed relieve the condition to a certain extent, but they are only used when patients have poor tolerance to NSAIDs and cannot ideally control the condition, or when patients develop peripheral arthritis.
In summary, the drug treatment of AS is extremely limited. Existing treatments are almost all aimed at "relieving symptoms" and have almost no effect on the patient's disease progression and etiology. Therefore, there is an urgent need for a series of specific drugs that can target its pathogenesis, delay the occurrence and development of the disease, or even cure it.
The era of targeted drugs: new hope emerges
With the improvement of basic medical level around the world, more and more information about the pathogenesis of AS has been revealed. In recent years, targeted innovative therapies represented by biological agents and targeted small molecule drugs have been introduced one after another, promoting the treatment of AS from symptom control to targeted therapy.
From the perspective of target action, the biological agents currently used to treat AS mainly include TNF-α inhibitors (etanercept, adalimumab, infliximab, etc.) and IL-17 inhibitors (secukinumab, ixekizumab, etc.), as well as small molecule drug JAK inhibitors (tofacitinib, upadacitinib, etc.).
In addition, the Expert Consensus on Long-term Management of Ankylosing Spondylitis points out that from the perspective of health economics, for patients in the active stage, biological agents are more economical and effective than traditional treatments such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and physical therapy. This has also led to an increase in the acceptance of targeted agents by AS patients in clinical practice, and the overall drug market size and research and development enthusiasm have also risen.
Three major targets lead the market launch
According to Yaozhi data statistics, there are currently more than 80 AS treatment drugs on the market worldwide, including 35 innovative AS biologics and small molecule targeted drugs, including 18 small molecule preparations, with targets including PTGS1/2, JAK1/2/3, etc.; and 17 biologics, with targets including IL17A, TNF-α, etc.
Among the AS therapeutic drugs that have entered the clinical stage and have been launched at home and abroad, the top ten targets in terms of pipeline quantity are all mature targets, and the product pipelines are all after clinical phase I, mainly including IL17A, PTGS1/2, JAK1, and PTGS1. Among them, IL17A target has 6 products launched, PTGS1/2 target has 5 products launched, JAK1 target has 4 products launched, and PTGS1 target has 5 products launched.
TNF-α, IL-17 and JAK1 are the most concentrated targets for the research and development of innovative drugs for the treatment of AS in China.
In terms of TNF-α inhibitors, the domestic market is currently dominated by generic drugs, and there are no domestically produced TNF-α inhibitor innovative drugs on the market. The overall market is saturated, and its high development costs and drug resistance and insufficient response problems also hinder the development of domestic innovative drugs. So far, there are 7 adalimumab, 4 etanercept, and 4 infliximab biosimilars on the market in China. And there is another more important reason why domestic pharmaceutical companies favor TNF-α inhibitor biosimilars, that is, in addition to AS, this type of drug is also relatively widely used in other autoimmune diseases, and the market space is larger (the total size of the Chinese market for TNF-α inhibitors has reached 5.5 billion yuan in 2023).
As for IL-17 inhibitors, they mainly inhibit pathological new bone formation by directly blocking the key pathways of bone destruction, and have more advantages in delaying the progression of imaging. Currently, the only domestic drugs include Hengrui Medicine's Fulanixzumab and Zhixiang Jintai's Celicizumab. Among them, Celici monoclonal antibody uses dual-carrier phage platform technology to stabilize drug molecules, prolong the duration of therapeutic effect and reduce the frequency of dosing, and has advantages in drug compliance. The humanized antibody structure also gives it a higher affinity for IL-17A than similar drugs, and it can more effectively block the IL-17A/IL-17R signaling pathway and enhance the bone destruction inhibition effect.
As for JAK inhibitors, as representatives of small molecules in targeted preparations, they make up for the shortcomings of biological preparations through the convenience of oral administration. Among them, emacitinib, by introducing a unique pharmacophore structure combination, acts more precisely on JAK1, and has significantly lower inhibitory effects on JAK2 and JAK3, significantly reducing adverse reactions of the hematopoietic system such as anemia and thrombocytopenia, which is conducive to long-term medication.
A plethora of new drugs
Progress in the development of innovative AS drugs
According to Yaozhi data, there are 43 AS treatment drug R&D pipelines in the clinical research stage worldwide, of which 33 are in China. Existing R&D pipelines at home and abroad are mostly concentrated in the late clinical stage, with 7 pipelines that have submitted clinical applications and 15 pipelines in clinical phase III.
Table: Domestic late clinical AS treatment drugs In this field in China, the pipelines entering the late clinical stages are gradually developing from TNF-α inhibitors to more trendy targets, including IL-17 inhibitors for biological agents and JAK inhibitors for small molecule agents.
Among them, LZM-012/XKH004, jointly developed by Livzon Pharmaceutical and Xinkanghe Biotechnology, is the fastest-progressing domestic IL-17A/F dual antibody, which blocks two pro-inflammatory factors at the same time. Its Phase III clinical trial for AS treatment successfully reached the clinical endpoint, showing best-in-class therapeutic potential, and its safety is comparable to the incidence of adverse events of similar drugs already on the market.
Technology + Market
AS has a clear future trend
Technology Trends:
Targeted drugs represented by TNF-α inhibitors, IL-17 inhibitors and JAK1 inhibitors are gradually replacing traditional non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and becoming the core treatment for AS.
In terms of biological preparations, compared with TNF-α inhibitors, IL-17 inhibitors can not only have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects, but also inhibit new bone formation and significantly improve long-term prognosis, making IL-17 the most deployed AS treatment drug target by domestic companies. Domestic drugs have improved their efficacy and safety through humanized antibody design, IL-17A/F bispecific antibodies and other technical optimizations. Currently, many domestic drug pipelines have been launched and entered the late clinical stage. It is expected that IL-17 inhibitors will be the main research and development direction of AS treatment drugs in the future.
In terms of small molecule targeted drugs, JAK1 inhibitors are convenient for oral administration, which is beneficial for the long-term treatment of AS patients. In addition, the drugs on the market and under development have overcome the lack of selectivity of traditional JAK targeted drugs. Some pipelines have been launched and entered the late clinical stage. In the future, JAK1 inhibitors will occupy a more important position in the field of AS treatment.
Market Trends:
The recent intensive approval of innovative domestic AS treatment drugs marks the transition of Chinese pharmaceutical companies from biosimilars to original research innovation. Domestic drugs have improved efficacy and safety through technical optimization such as humanized antibody design, while significantly reducing treatment costs. Frontier directions such as bispecific antibodies also provide new paths for conquering refractory AS. In the future, as more domestic drugs are launched, the field of AS targeted treatment drugs will gradually achieve domestic substitution, while the penetration rate will be further improved and the market size will continue to grow.
In terms of generic drugs, the market for TNF-α inhibitor generic drugs is currently saturated due to low-price competition from domestically produced drugs, which has forced original research drugs to reduce their prices, improving the accessibility of TNF-α inhibitors and promoting market development; with the expiration of patents for target drugs such as IL-17, the development of related biosimilars and small molecule generic drugs may be accelerated. Driven by policies, centralized medical insurance procurement continues to lower prices and more widely improve the accessibility of AS treatment drugs.
summary
Ankylosing spondylitis is a difficult-to-treat autoimmune disease with more than 4 million patients worldwide, a high disability rate and an urgent need for treatment. Traditional drugs (NSAIDs, etc.) can only relieve symptoms but cannot prevent disease progression.
In recent years, targeted biological agents such as TNF-α, IL-17, and JAK inhibitors have gradually become core therapies. Domestic IL-17 and JAK inhibitor innovative drugs have broken the import monopoly with technological breakthroughs, and domestic TNF-α generic drugs have forced original research drugs to reduce prices through low-price competition, promoting the improvement of drug accessibility.
In the future, AS treatment will develop towards targeted and universalization.
https://news.yaozh.com/archive/45447.html
By editorRead more on
- Rovaxitinib approved for marketing, filling the demand for myelofibrosis treatment March 2, 2026
- Warrant Pharmaceuticals’ active pharmaceutical ingredient receives Brazil’s first official GMP certification March 2, 2026
- Merck’s New Story March 2, 2026
- Rongchang Biotechnology has turned a profit! March 2, 2026
- Jiuyuan Gene’s “Simeglucopyranoside” for weight loss (Jikeqin®) has been submitted for market approval March 2, 2026
your submission has already been received.
OK
Subscribe
Please enter a valid Email address!
Submit
The most relevant industry news & insight will be sent to you every two weeks.



