Robotic diagnosis and treatment is reaching a turning point towards widespread adoption.
January 23, 2026
Source: drugdu
 32
32
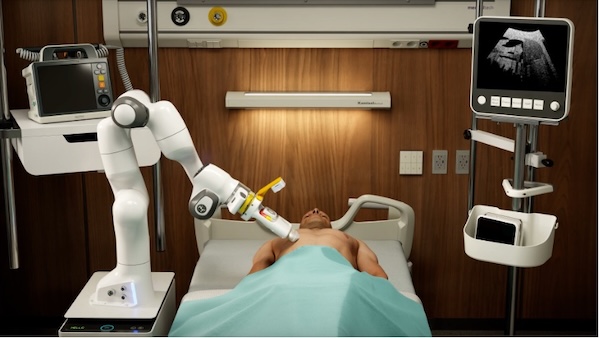 In today's rapidly developing technological landscape, robots are integrating into the field of surgical diagnosis and treatment at an unprecedented pace, bringing patients a more precise and safer medical experience and providing doctors with stronger technical support. However, the lack of unified standards for the pricing mechanisms of innovative medical services has, to some extent, affected their clinical promotion and sustainable development. On December 5, 2025, the National Healthcare Security Administration issued the "Guidelines for the Establishment of Pricing Items for Surgical and Treatment Assistance Medical Services (Draft for Comments)" to provincial healthcare security bureaus for internal feedback within the healthcare security system. This marks the first time that the pricing mechanisms for innovative medical services such as surgical robots have been systematically standardized at the national level.
In today's rapidly developing technological landscape, robots are integrating into the field of surgical diagnosis and treatment at an unprecedented pace, bringing patients a more precise and safer medical experience and providing doctors with stronger technical support. However, the lack of unified standards for the pricing mechanisms of innovative medical services has, to some extent, affected their clinical promotion and sustainable development. On December 5, 2025, the National Healthcare Security Administration issued the "Guidelines for the Establishment of Pricing Items for Surgical and Treatment Assistance Medical Services (Draft for Comments)" to provincial healthcare security bureaus for internal feedback within the healthcare security system. This marks the first time that the pricing mechanisms for innovative medical services such as surgical robots have been systematically standardized at the national level.
Robotic diagnosis and treatment has become a powerful tool for solving clinical pain points.
"Early diagnosis of lung cancer has always been a challenge in clinical practice," Dr. Liao Huai, Deputy Director of the Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine at the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, told reporters. Traditional percutaneous lung biopsy has a high incidence of pneumothorax and can even lead to fatal bleeding; while traditional bronchoscopy can only reach about level four bronchi, limiting its ability to diagnose early peripheral lung cancer. "The emergence of shape-sensing bronchoscopy robots has brought hope for solving these problems," Dr. Liao pointed out. According to the "Expert Consensus on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Lung Nodules with Shape-Sensing Bronchoscopy Robots" released in June 2025, the core innovation of shape-sensing bronchoscopy robots lies in embedding shape-sensing fiber optic sensors throughout the duct, enabling real-time and precise monitoring of the duct's three-dimensional morphology and position within the complex bronchial tree, essentially equipping doctors with "X-ray vision" and "stabilizing hands." It boasts significant advantages in precision, stability, and safety, achieving millimeter-level accuracy. The robotic arm enables fine-tuning, and the catheter, only 3.5mm in diameter, can penetrate into bronchi of level seven and above, reaching within approximately 25px of a lung nodule. The bronchoscope robot's catheter is stably positioned towards the lung nodule, enabling precise close-range biopsy and significantly improving diagnostic rates. Simultaneously, this robot reduces the overall complication rate of lung cancer diagnosis to 1% or even lower, allowing patients to receive accurate diagnosis and radical treatment even in the early stages of lung cancer.
In the field of laparoscopic surgery, laparoscopic surgical robots have gained favor among surgeons. Professor Chen Lingwu, director of the Department of Urology at the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, pointed out that compared with traditional open surgery and laparoscopic surgery, robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery is less invasive, has less bleeding, manageable risks, less pain, faster recovery, and shorter hospital stays, and performs particularly well in terms of functional preservation.
Achieving a win-win situation of patient benefit and improved medical efficiency.
For patients, the application of robotics technology has brought tangible benefits. Shape-aware bronchoscopy robots are considered one of the most advanced bronchoscopic navigation technologies currently available. Professor Liao Huai stated, "Shape-aware bronchoscopy robots allow lung cancer patients to receive accurate diagnosis and treatment at an early stage, avoiding the high costs of late-stage treatment and unnecessary lung tissue resection, effectively protecting patients' lung function and quality of life." Robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery reduces patient suffering, shortens hospital stays, lowers the incidence of postoperative complications, and improves patients' quality of life. Data from a 12-year study covering 22 countries and encompassing over 1 million cases across seven surgical procedures showed that robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery had a 56% lower surgical conversion rate than laparoscopy, a 21% lower bleeding rate than laparoscopy and a 75% lower bleeding rate than open surgery, a 10% lower complication rate after 30 days than laparoscopy and a 44% lower complication rate than open surgery, and a 0.5-day shorter hospital stay than laparoscopy and a 1.9-day shorter hospital stay than open surgery. These data fully demonstrate the significant clinical value of robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery in improving surgical safety and effectiveness.
Meanwhile, robotics technology also provides doctors with stronger technical support. Professor Chen Lingwu pointed out that robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery has expanded the scope of surgery, enabling doctors to perform complex surgeries that were previously considered too risky for minimally invasive procedures. Three-dimensional magnification, high degree of freedom in instrument manipulation, no blind spots, and anti-shake functionality make the surgery more precise; at the same time, robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery reduces occupational hazards for doctors and extends their careers. "An elderly urologist in his seventies or eighties in the United States, with the help of the robot's anti-shake function and precise operation, was still able to perform high-quality surgeries on the front lines, even though he suffered from Parkinson's disease."
A reasonable pricing system promotes sustainable technological development.
Currently, the costs associated with robotic surgery are not fully covered by medical insurance, and some expenses must be paid out of pocket, which limits its widespread adoption. Professor Liao Huai believes that from the patient's perspective, medical insurance coverage can prevent patients from forgoing robotic treatment due to high out-of-pocket costs, allowing them to receive precise diagnosis and treatment in the early stages of disease, reducing the high costs of late-stage treatment and unnecessary tissue removal, and protecting patients' health and quality of life. "The ideal pricing system should be affordable for the government, the public, businesses, and hospitals, forming a virtuous cycle of sustainable development," he further pointed out. Medical insurance coverage not only reduces the economic burden on patients and allows more people to benefit from advanced medical technology, but also incentivizes companies to continuously innovate and develop, driving technological updates and iterations.
Professor Chen Lingwu also emphasized that the pursuit of low prices should not be the sole focus; rather, prices should be within a reasonable range, benefiting patients while encouraging innovation and research by companies, thus creating a virtuous cycle. Shanghai has already included some robotic surgery procedures in its medical insurance program, alleviating the financial burden on patients and promoting the widespread adoption of robotic surgery. In the future, with the continuous maturation of technology and further improvements in medical insurance policies, robotic technology is expected to be widely used in more departments.
Robotic diagnosis and treatment will become more widespread in the future.
How will robotics technology develop in the field of medical diagnosis and treatment in the future?
Professor Liao Huai stated that current shape-sensing bronchoscopy robots primarily focus on the precise diagnosis of pulmonary nodules, and in the future, they can achieve a one-stop closed-loop operation of diagnosis and treatment. For high-risk pulmonary nodules with a high probability of malignancy, precise cryoablation or radiofrequency ablation can be performed with robot assistance to achieve radical cure, avoid unnecessary segmentectomy or lobe resection, and preserve lung function to the maximum extent.
"Robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery will become more widespread in the future, and may even replace traditional laparoscopic surgery," Professor Chen Lingwu pointed out. Taking urology as an example, robotic surgeries currently account for more than 50% of the department's surgeries. In the future, almost all urological surgeries will rely on robotic technology, and more and more doctors will realize that mastering robotic technology is an essential quality for surgeons.
Surgical robots are essentially advanced assistants to doctors, but the entire surgical process remains doctor-led, making talent development paramount. Moreover, as robotic technology continues to evolve, with more intelligent navigation systems and more precise instruments, doctors need to continuously learn and master new skills. Professor Chen Lingwu stated that the widespread adoption of robotic technology requires a large number of doctors with relevant skills. Through standardized training, more doctors can utilize robotic platforms to improve their diagnostic and treatment capabilities, narrowing the technological gap between hospitals and enabling patients in rural areas to enjoy high-quality medical services.
https://news.yaozh.com/archive/46983.html
By editorRead more on
- RiboBio’s ApoC3-Targeting siRNA Drug RBD5044 Granted Implicit Approval for Phase II Clinical Trials in China January 23, 2026
- A new generation of ophthalmic dual antibodies challenges Roche’s dominant position. January 23, 2026
- Leading CRO company sees net profit surge 1468% January 23, 2026
- The Phase 1 clinical trial showed amazing results, causing the stock price to surge by 166%. January 23, 2026
- Wanshuan® (aniline profen injection) is Yiling Wanzhou’s first approved patented new chemical drug. January 23, 2026
your submission has already been received.
OK
Subscribe
Please enter a valid Email address!
Submit
The most relevant industry news & insight will be sent to you every two weeks.



