A Comparative Overview of the US, EU, China, India and Brazil
December 3, 2025
Source: drugdu
 150
150

Against the backdrop of rapid internationalization of pharmaceutical formulations, pharmaceutical excipients – as critical components supporting drug quality and stability – are receiving increasing attention in regulatory frameworks worldwide.
For excipient manufacturers planning to expand into overseas markets, understanding the compliance thresholds and regulatory focus of major markets is a necessary prerequisite for designing a global export strategy.
Drawing on practical registration experience and international regulatory practices, we compare excipient regulations across five key markets – the United States, the European Union, China, India and Brazil – to help companies build a global compliance framework for excipients.
At a Glance: Regulatory Requirements Across Five Major Markets
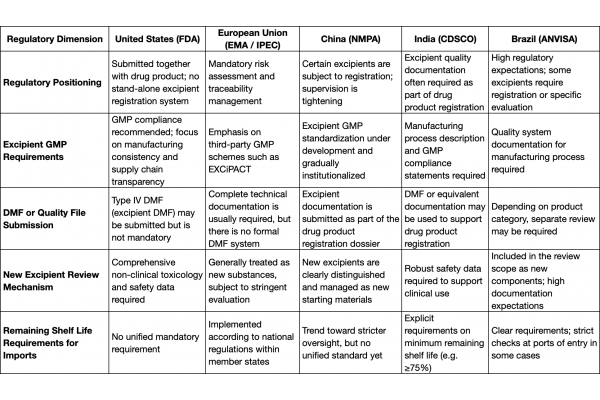
Regional Regulatory Focus – Detailed Analysis
United States: Well-established DMF system with emphasis on data transparency
The FDA reviews excipients in the context of finished drug product applications. Manufacturers may choose to submit a Type IV DMF (Drug Master File for excipients). Although it is not mandatory, a DMF can significantly enhance the attractiveness of a supplier to formulation manufacturers.
Regulatory attention is focused on whether the excipient is listed in the Inactive Ingredient Guide (IIG) and whether the manufacturer can provide complete information on manufacturing processes, quality control and stability. For new excipients, the FDA requires comprehensive safety packages, including toxicology and non-clinical data, to support their use.
European Union: Risk assessment is mandatory, and quality systems are central
Since the implementation of Directive 2011/62/EU, risk assessment for excipients has become a legal obligation in the EU. Companies must perform detailed risk assessments considering the excipient’s function, frequency of use, origin and history, and complement this with supplier qualification and audits.
The IPEC Europe framework and EXCiPACT GMP certification enjoy wide recognition in the EU and can substantially improve market access efficiency. For functional or novel excipients, the EMA typically applies an assessment standard similar to that used for new active substances.
China: Regulatory oversight is tightening, with the framework still evolving
In recent years, the NMPA has continuously strengthened the supervision of excipients. Some excipients have been brought under categorized registration management, and companies are encouraged to submit excipient technical documentation in line with drug product consistency evaluation requirements.
Excipient GMP systems are being developed and are expected to be more closely integrated with drug product supervision in the future. In practice, excipients are often submitted together with the drug product for review, and must be supported by documentation on stability, process control and compliance with established standards.
India: Strong emphasis on traceability and remaining shelf life
Although India does not have a stand-alone excipient registration framework, it imposes relatively stringent requirements on imported excipients. In particular, with respect to timing of import, regulations often stipulate that the product’s remaining shelf life must not fall below a specified threshold (e.g. ≥75% of the original shelf life).
In addition, excipient documentation must be submitted as part of the drug product registration package, covering origin, manufacturing process and batch-to-batch consistency.
Brazil: Complex compliance pathways with focus on registration and actual remaining shelf life
ANVISA adopts a category-based approach when reviewing imported excipients. Some new excipients or those used in specific formulations are required to undergo separate registration.
Similar to India, remaining shelf life is a key regulatory concern. In many settings, imported excipients must have at least around 80% remaining shelf life upon arrival at the port of entry. During registration, applicants are required to submit comprehensive documentation on quality control systems.
Recommendations for Excipient Manufacturers: Build Global Markets Starting from Compliance
Build standardized excipient documentation packages: Include, where applicable, DMFs, stability data, quality standards, MSDS, safety studies and other relevant documentation to accommodate the expectations and review habits of different regulators.
Prioritize GMP or equivalent quality certifications: Obtain certifications such as EXCiPACT or IPEC-PQG GMP, to enhance trust among international buyers and improve market access.
Focus on priority markets and expand step by step: Consider entering markets with clearer regulatory pathways and more open review windows first, such as Southeast Asia, Latin America and South Africa, and then gradually move into major markets like Europe and the United States.
Leverage digital B2B platforms to expand overseas channels: Use B2B platforms to support multi-language product presentation, visibility of registration and quality credentials, and data-driven marketing. This can significantly reduce the cost of customer acquisition and exposure for small and medium-sized enterprises.
Drugdu.com has long focused on the globalization journey and regulatory challenges of excipient manufacturers. The platform has already brought together hundreds of excipient and API suppliers and supports buyer access and inquiry matching from more than 220 countries and regions.
If you would like to better understand buyer preferences for excipients in different countries, trending search keywords, or regulatory and registration trends, you are welcome to join Drugdu.com and help us build a global ecosystem for pharmaceutical excipients.
By editorRead more on
- Kanghua Biologics Faces Formidable Challenges in mRNA Vaccine Development February 6, 2026
- Aligning with international standards! Aidea Pharma obtains Tanzania’s ML3 GMP certification February 5, 2026
- Shijiazhuang Pharmaceutical Group’s clopidogrel emulsion injection has received a drug registration certificate. February 5, 2026
- Human Coagulation Factor IX Drug Registration and Marketing Authorization Application Accepted February 5, 2026
- HX111 completes first patient dosing in Phase I clinical trial February 5, 2026
your submission has already been received.
OK
Subscribe
Please enter a valid Email address!
Submit
The most relevant industry news & insight will be sent to you every two weeks.



