Yuheng Biotechnology announces the release of APHEXDA (Antifotide) ®, Motixafortide has been approved for marketing by the Macau Drug Administration in China
September 23, 2024
Source: drugdu
 548
548
Motefutide Macau officially approvedOn September 20, 2024, Guangzhou
 Yuheng Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (referred to as "Yuheng Biotechnology") announced the world's first peptide drug, Mortifutide (APHEXDA), targeting the chemokine receptor 4 (CXC chemokine receptor 4, CXCR4) ®, Motixafortide has recently been officially approved for marketing by the Drug Administration of the Macao Special Administrative Region of China. According to the WHO ATC (Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System) drug classification management system, it has been approved as immune enhancer L03AX23, which is used in combination with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) to mobilize hematopoietic stem cells for peripheral blood stem cell collection and subsequent autologous transplantation in patients with multiple myeloma (MM). After Boao, Hainan, Macau has become the second region within Yuheng Biotech's Asia authorized area to receive approval for Motefutide. Motefutide has obtained new drug approval in the United States in September 2023. It is the first approved innovative drug for multiple myeloma stem cell mobilization in the United States since 2008, and also the first peptide drug targeting CXCR4 to be successfully marketed.
Yuheng Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (referred to as "Yuheng Biotechnology") announced the world's first peptide drug, Mortifutide (APHEXDA), targeting the chemokine receptor 4 (CXC chemokine receptor 4, CXCR4) ®, Motixafortide has recently been officially approved for marketing by the Drug Administration of the Macao Special Administrative Region of China. According to the WHO ATC (Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System) drug classification management system, it has been approved as immune enhancer L03AX23, which is used in combination with granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) to mobilize hematopoietic stem cells for peripheral blood stem cell collection and subsequent autologous transplantation in patients with multiple myeloma (MM). After Boao, Hainan, Macau has become the second region within Yuheng Biotech's Asia authorized area to receive approval for Motefutide. Motefutide has obtained new drug approval in the United States in September 2023. It is the first approved innovative drug for multiple myeloma stem cell mobilization in the United States since 2008, and also the first peptide drug targeting CXCR4 to be successfully marketed.

According to the ATC coding rules of WHO, the L03A subgroup belongs to immune enhancers; For new molecular drugs that do not belong to any existing treatment classification, the 4th level code will be assigned to Group X. Motefutide has been awarded the code L03AX23, level 4 as X, indicating that it does not belong to any existing level 4 treatment classification. Motefutide has become the first CXCR4 peptide drug to be included in the ATC classification system by WHO, and is a pioneering new drug.
Accelerate the benefits for Chinese patients
Since the official implementation of the "Hong Kong Macau Medical Device Connect" policy in 2021, it has opened up a channel for international advanced and innovative drugs and devices to quickly enter clinical applications. Drugs approved for market in Hong Kong and Macau can be used in designated medical institutions in the Greater Bay Area, bringing treatment convenience to residents in the Greater Bay Area. As of 2024, a total of 19 designated medical institutions have been approved through the "Hong Kong Macau Medical Device Connect" policy, covering 9 cities in the Guangdong Hong Kong Macau Greater Bay Area: Guangzhou, Shenzhen, Zhuhai, Foshan, Huizhou, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Jiangmen, and Zhaoqing.
Relying on favorable policies such as the "Hong Kong Macao Pharmaceutical Equipment Connect" in Guangdong Hong Kong Macao Greater Bay Area and the licensed medical equipment in Hainan Boao Lecheng Pilot Area, Yuheng Biology will accelerate the accessibility of this innovative drug in the field of multiple myeloma treatment and stem cell transplantation in patients in Chinese Mainland. Based on the expected no racial differences in the globally approved multicenter Phase III GENESIS study, Yuheng Biotechnology was approved by the Drug Evaluation Center of the National Medical Products Administration in May this year to conduct a bridging Phase III clinical study. In June, it will officially land in the Boao Lecheng Pilot Zone and will first be applied for clinical use in the Boao Super Hospital. And at the same time, the new drug market registration application in Singapore was initiated.
Innovative CXCR4 peptide drugs
In the bone marrow microenvironment, CXCR4 and stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1/CXCL12) play important roles in the homing and residence of hematopoietic stem cells, as well as regulating the distribution of immune cells. Hematopoietic stem cells are anchored in the bone marrow matrix through the interaction between CXCR4 and SDF-1/CXCL12. Motefutide is a subcutaneous CXCR4 antagonist with an innovative cyclic peptide structure with high affinity, receptor occupancy time exceeding 72 hours, and prolonged in vivo activity. Motefutide binds to the CXCR4 receptor on the surface of stem cells through six sites, precisely blocking the interaction between CXCR4 and SDF -/CXCL12, causing stem cells to lose anchoring and migrate from the bone marrow to the peripheral blood, thereby significantly increasing the collection of CD34+cells, shortening the collection cycle, reducing the number of collections, and increasing the success rate of transplantation. Simultaneously regulating the migration and activation of immune cells, affecting the immune response of the body.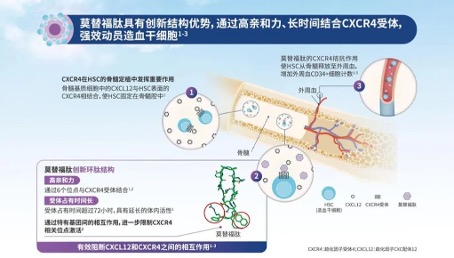 The approval of metoclopramide is based on the results of the GENESIS Global Multicenter Phase 3 Registry Study (NCT03246529), which aims to compare the safety and efficacy of metoclopramide+G-CSF with placebo+G-CSF in MM patients who received hematopoietic stem cell mobilization prior to autologous hemp top stem cell transplantation (ASCT). This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study achieved all primary and key secondary endpoints, with good safety and tolerability. The research results have been published in the journal Nature Medicine. This clinical study shows that moxifloxacin+G-CSF can efficiently mobilize stem cells. With only one dose of medication, 88.8% of patients can obtain the ideal dose of 6 × 106/kg body weight CD34+cells through one single collection, and 92.5% of patients can obtain it through a maximum of two single collections; The proportion of patients receiving placebo+G-CSF was 9.5% (OR 118.0, 95% CI 25.36-549.35, P<0.0001) and 26.2% (OR 53.3, 95% CI 14.12-201.33, P<0.0001), respectively. Motefutide significantly improved the efficiency and quality of hematopoietic stem cell collection, laying the foundation for successful transplantation.
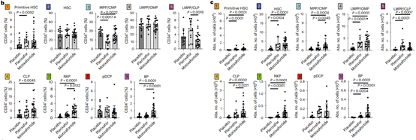
The approval of metoclopramide is based on the results of the GENESIS Global Multicenter Phase 3 Registry Study (NCT03246529), which aims to compare the safety and efficacy of metoclopramide+G-CSF with placebo+G-CSF in MM patients who received hematopoietic stem cell mobilization prior to autologous hemp top stem cell transplantation (ASCT). This randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study achieved all primary and key secondary endpoints, with good safety and tolerability. The research results have been published in the journal Nature Medicine. This clinical study shows that moxifloxacin+G-CSF can efficiently mobilize stem cells. With only one dose of medication, 88.8% of patients can obtain the ideal dose of 6 × 106/kg body weight CD34+cells through one single collection, and 92.5% of patients can obtain it through a maximum of two single collections; The proportion of patients receiving placebo+G-CSF was 9.5% (OR 118.0, 95% CI 25.36-549.35, P<0.0001) and 26.2% (OR 53.3, 95% CI 14.12-201.33, P<0.0001), respectively. Motefutide significantly improved the efficiency and quality of hematopoietic stem cell collection, laying the foundation for successful transplantation.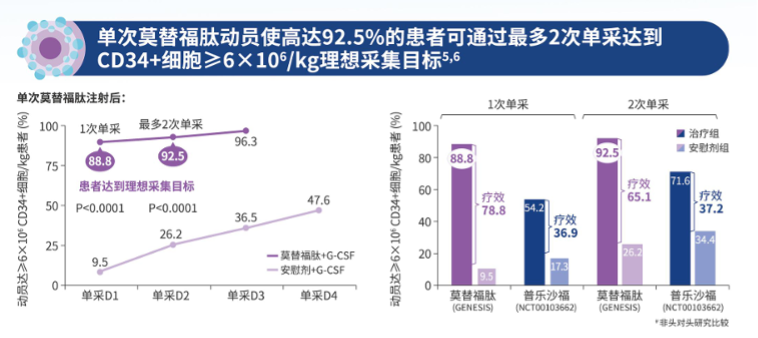 Meanwhile, this study showed that moxifloxacin+G-CSF significantly increased the percentage of common lymphoid progenitor cells (CLP), natural killer cell precursors (NKP), and eosinophil precursors (BP). Compared with the small molecule CXCR4 blocker plerixafor+G-CSF, moxifloxacin+G-CSF significantly increased the percentage of multipotent progenitor cells and common myeloid progenitor cells (MPP/CMP), NKP, and BP. Quantitative analysis of the absolute number of hematopoietic stem cell and progenitor cell (HSPC) subpopulations showed that compared to placebo+G-CSF, the absolute number of hematopoietic progenitor cells mobilized by moxifloxacin+G-CFS was 10.5 times higher. Compared with Plexafoc+G-CSF, Motesafoc+G-CSF significantly increased the number of MPP/CMP, CLP, and BP. These data indicate that moxifloxacin induces the full mobilization of multiple HSPC subgroups, which can undergo extensive multi lineage hematopoietic reconstruction.
Meanwhile, this study showed that moxifloxacin+G-CSF significantly increased the percentage of common lymphoid progenitor cells (CLP), natural killer cell precursors (NKP), and eosinophil precursors (BP). Compared with the small molecule CXCR4 blocker plerixafor+G-CSF, moxifloxacin+G-CSF significantly increased the percentage of multipotent progenitor cells and common myeloid progenitor cells (MPP/CMP), NKP, and BP. Quantitative analysis of the absolute number of hematopoietic stem cell and progenitor cell (HSPC) subpopulations showed that compared to placebo+G-CSF, the absolute number of hematopoietic progenitor cells mobilized by moxifloxacin+G-CFS was 10.5 times higher. Compared with Plexafoc+G-CSF, Motesafoc+G-CSF significantly increased the number of MPP/CMP, CLP, and BP. These data indicate that moxifloxacin induces the full mobilization of multiple HSPC subgroups, which can undergo extensive multi lineage hematopoietic reconstruction.
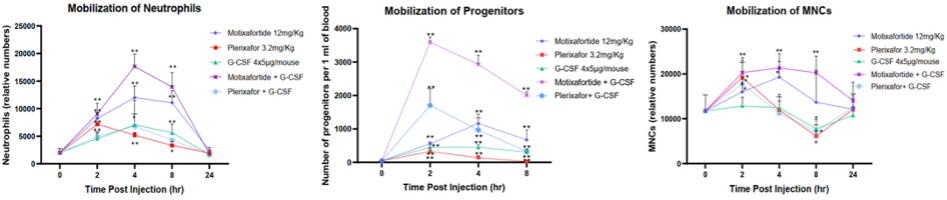
Another study also showed that whether used alone or in combination with G-CSF, the efficacy of metoclopramide is significantly better than that of propranolol. It can quickly mobilize cells (neutrophils, monocytes, and hematopoietic progenitor cells) into peripheral blood and maintain a high mobilization level within 24 hours after injection.
The broad application prospects of CXCR4
Based on the biological mechanism and extensive preclinical and clinical exploration of moxifloxacin, this drug also has broader application potential, such as showing significant synergistic and attenuated effects in tumor immunotherapy and radiochemotherapy, as well as enhancing the immunity of high-risk and immunocompromised populations.
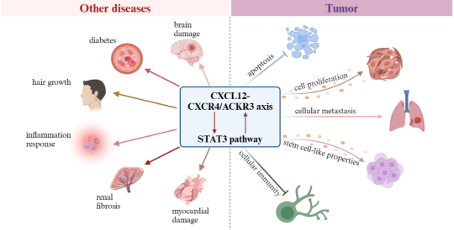
Tumor immunotherapy
CXCR4 is expressed on various immune cells and participates in regulating the migration, activation, and function of immune cells. Motefutide can affect the distribution and activation status of immune cells in the body by blocking CXCR4, reducing the aggregation of immunosuppressive cells in the tumor microenvironment, and increasing the infiltration of anti-tumor immune cells such as effector T cells, thereby enhancing the body's anti-tumor immune response. When used in combination with immunotherapy and other therapies, Motifudine significantly improves the intensity and durability of the anti-tumor response, makes "cold" tumors (such as pancreatic cancer) "hot", and improves the treatment sensitivity. A phase II clinical study (CheMo4METPANC, NCT04543071) on the combination of motiflutide, PD-1 inhibitor and standard chemotherapy in the treatment of first-line pancreatic cancer was released at the 2023 AACR meeting. The study showed that among the 11 patients enrolled in the exploratory phase, the overall response rate (ORR) was 64%; The median progression free survival (mPFS) is 9.6 months, and the disease control rate (DCR) is 82%.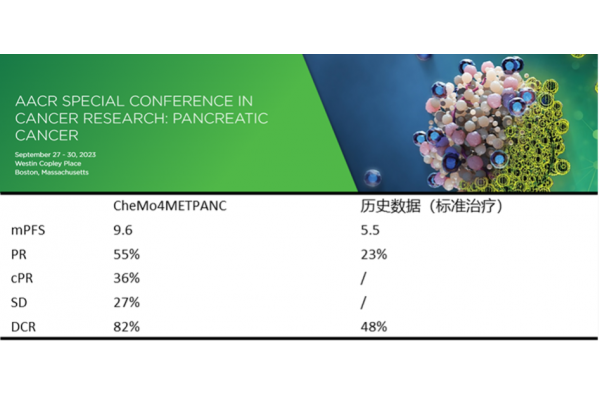 At the same time, CXCR4 is highly expressed in 75% of tumor cells, including pancreatic cancer, breast cancer, gastric cancer, prostate cancer, kidney cancer, etc., and is associated with tumor chemotaxis, invasion, angiogenesis and cell proliferation. Inhibiting CXCR4 can suppress the migration of tumor cells, the escape of cancer cells during treatment, and the inhibition of angiogenesis, and has multiple mechanisms of anti-tumor potential.
At the same time, CXCR4 is highly expressed in 75% of tumor cells, including pancreatic cancer, breast cancer, gastric cancer, prostate cancer, kidney cancer, etc., and is associated with tumor chemotaxis, invasion, angiogenesis and cell proliferation. Inhibiting CXCR4 can suppress the migration of tumor cells, the escape of cancer cells during treatment, and the inhibition of angiogenesis, and has multiple mechanisms of anti-tumor potential.
Adjuvant drugs for radiotherapy and chemotherapy
During the process of radiotherapy and chemotherapy, preliminary studies have shown that moxifloxacin not only enhances the killing effect of radiotherapy and chemotherapy on tumor cells, but also improves patient tolerance and quality of life by reducing side effects such as neutropenia caused by treatment. In non clinical studies, it has been found that moxifloxacin has a positive effect on the recovery of chemotherapy-induced blood cell reduction and thrombocytopenia, and can stimulate the generation of megakaryocytes and platelets. After a single administration, an increase in progenitor cells and platelets can be observed, and the effect is further enhanced after repeated administration. Non clinical studies have also found that CXCR4 inhibitors may reverse immune checkpoint drug-induced cardiac toxicity.
Immune repair
In populations at high risk of infection or with weakened immunity, moxifloxacin not only increases the number of immune cells in peripheral blood by mobilizing hematopoietic stem cells, but also promotes the regeneration and proliferation of immune cells, increasing the number of important immune cells such as T cells, B cells, NK cells, and neutrophils in peripheral blood, which helps enhance the body's defense against pathogens and tumor cells.
Autoimmune and fibrotic diseases
Autoimmune diseases are usually accompanied by abnormal activation and improper migration of immune cells. CXCR4 inhibitors can reduce the aggregation of immune cells at the site of inflammation and alleviate autoimmune reactions by blocking the interaction between CXCR4 and its ligand SDF-1. Preliminary studies in vitro and animal models have shown that CXCR4 inhibitors may have certain effects on diseases such as psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, pulmonary fibrosis, and rheumatoid arthritis.
Motefutide exhibits unique biological mechanisms and broad clinical application potential in hematopoietic stem cell mobilization, immune cell regulation, and other areas by precisely blocking the interaction of CXCR4-SF-1/CXCL12 axis. With the continuous deepening of research and the expansion of clinical applications, moxifloxacin is expected to bring good news to more patients and populations.
Based on the characteristics of the action mechanism of Motifudine and the existing clinical data, Yuheng Biological plans to develop other potential indications in solid tumor and cell therapy, including the combination of self developed whole human PD-1 monoclonal antibody cyparimab for the treatment of first-line pancreatic cancer. Other potential indications include mobilization of CD34+cells in cell therapy, improvement of bone marrow suppression by chemotherapy drugs, elevation of white blood, immune repair, etc.
Clinical demand for treatment of multiple myeloma
Multiple myeloma is the second most common blood malignancy. Asia has a large population, with 51400 new cases in 2022. The incidence rate in China is about 1.6/100000, and the incidence rate is increasing year by year. GLOBOCAN reports that China sees approximately 20000 new patients and 15000 deaths annually. According to Cancer Statistics Review, it is estimated that the total number of patients in China will exceed 100000.
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is a treatment method for rebuilding normal hematopoietic and immune function in patients, and is a very important treatment option for MM patients. The 2023 CSCO Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation Guidelines for the first time include autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in transplantation guidelines and provide detailed recommendations for its application in multiple myeloma. According to the NCCN guidelines for the treatment of multiple myeloma and the Chinese guidelines, autologous stem cell transplantation is a standard treatment for multiple myeloma and provides long-term survival opportunities for patients with this cancer.
Due to the extremely low content of hematopoietic stem cells in peripheral blood, mobilization is necessary to release hematopoietic stem cells from the bone marrow into peripheral blood, in order to achieve sufficient white blood cell count and CD34+cell count, and then obtain them through blood cell separation and collection techniques. The guidelines suggest that it is best to collect stem cells for two transplants at once to prepare for a second or future transplant, and research has shown that the number of transplanted stem cells is positively correlated with patient prognosis.
At present, the recommended minimum dose of autologous peripheral blood stem cells for a single ASCT is 2 × 106/kg body weight CD34+cells, and the ideal dose is ≥ 5 × 106/kg body weight CD34+cells [1]. The ideal dose of CD34+cells can accelerate hematopoietic reconstruction, reduce the occurrence of treatment-related complications, and decrease the need for blood transfusions. The traditional initial mobilization plan is to use granulocyte colony-stimulating factor G-CSF alone or in combination with chemotherapy, and 32% of lymphoma and 14% of MM patients cannot mobilize and collect the lowest dose of CD34+cells [2]. Patients who failed the initial mobilization need to be mobilized again, while the failure rate of traditional mobilization methods exceeds 70% [3]. The failure of mobilization severely limits the treatment of related diseases by ASCT. Therefore, transplantation requires higher demands for stem cell mobilizers, and drugs with good mobilization activity can significantly reduce the risk and burden of ASCT.
Read more on
- 20-Valent Pneumococcal Vaccine Approved for Clinical Trials January 20, 2026
- ADC205 Tablets Received Approval for Drug Clinical Trial January 20, 2026
- Sifang Optoelectronics makes strategic investment in Changhe Biotechnology January 20, 2026
- Mingde Bio plans to acquire a 51% stake in Hunan Lanyi through capital increase and acquisition January 20, 2026
- accelerating the transition of CLL treatment into a “chemotherapy-free era”. January 20, 2026
your submission has already been received.
OK
Subscribe
Please enter a valid Email address!
Submit
The most relevant industry news & insight will be sent to you every two weeks.



